The UK’s nuclear output has plunged to its lowest degree since 1982, Carbon Transient evaluation exhibits.
The 9% drop in 2021, attributable to retirements and outages on the UK’s ageing reactors, contributed to a report 17 terawatt hour (TWh) fall in low-carbon electrical energy final 12 months, with wind technology additionally falling 15%.
The federal government goals to have a absolutely decarbonised energy system by 2035 – however the newest figures present it’s going within the fallacious path. The figures are primarily based on Carbon Transient evaluation of information from BM Stories and the Division of Enterprise, Vitality and Industrial Technique (BEIS).
They present that the carbon depth of electrical energy technology rose final 12 months by practically 10% to 199 grams of carbon dioxide (CO2) per kilowatt hour (gCO2/kWh), up from a record-low 183gCO2/kWh in 2020.
It’s because electrical energy technology from fossil fuels was some 9% larger than a 12 months earlier, of which practically 90% got here from larger fuel output. Coal’s share remained under 2%, regardless of rising barely in contrast with a 12 months earlier, whereas fuel elevated its share from 34% to 37%.
However – with demand barely recovering from coronavirus lockdowns in 2020 – low-carbon sources nonetheless generated greater than half of UK electrical energy in 2021, together with 19% from wind, 14% from nuclear, 12% from biomass and 4% from photo voltaic.
Plunging nuclear
Many current headlines have centered on Germany’s deliberate technique to finish its use of nuclear energy, with three of its remaining six reactors having switched off firstly of the 12 months.
Few, although, have famous the numerous declines in nations together with France and the UK – albeit pressured moderately than attributable to coverage decisions – as ageing reactors come to the tip of their lives.
Electrical energy technology from the UK’s nuclear energy vegetation fell by one other 9% in 2021 to only 46TWh, lower than half the height in 1998 and the bottom in practically 4 a long time.
That is proven within the determine under, which charts the growth and subsequent decline of the UK’s nuclear output.
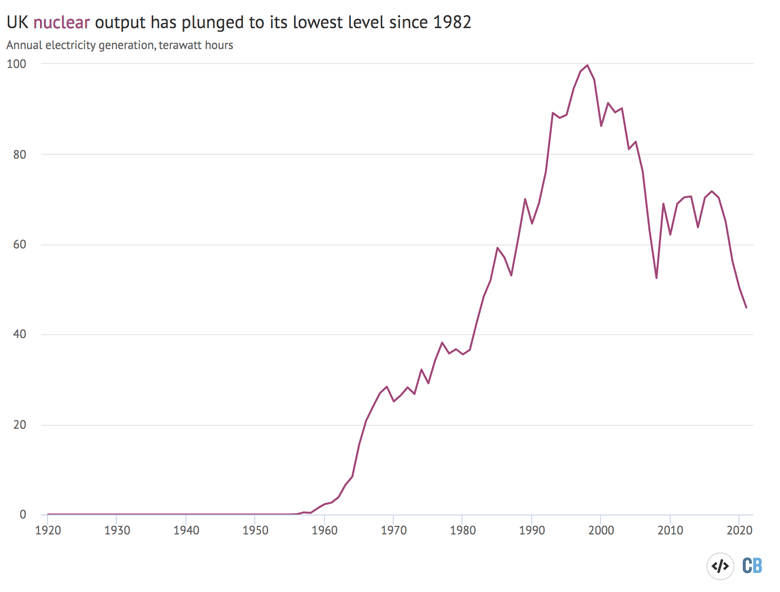
Electrical energy technology from nuclear energy vegetation within the UK, terawatt hours (TWh), 1920-2021. Supply: BEIS and Carbon Transient evaluation. Chart by Joe Goodman for Carbon Transient utilizing Highcharts.
Electrical energy technology from the present UK nuclear fleet is about to decline additional because the reactors attain their scheduled retirement, with all besides Sizewell B in Suffolk attributable to shut by 2030.
Two new reactors at Hinkley Level C in Somerset are attributable to come on-line later this decade and the federal government hopes to safe a deal for an similar plant at Sizewell C throughout this parliament.
Collectively, these new nuclear vegetation would roughly change present nuclear output.
(The federal government can also be supporting the event of small nuclear reactors, the primary of which it hopes to see coming on-line within the “early 2030s”.)
Low-carbon low
The UK’s windfarms additionally had a difficult 12 months in 2021, with technology falling by an estimated 15% – regardless of rising capability – on account of the bottom common windspeeds in a decade.
Lowered sunshine hours and below-average rainfall triggered 9% and 26% drops in photo voltaic and hydro technology, respectively, with the reported capability of each sources barely altering.
Together with the decline in nuclear output, this implies the UK’s low-carbon electrical energy technology noticed its largest ever one-year fall of 17TWh, proven within the chart under.
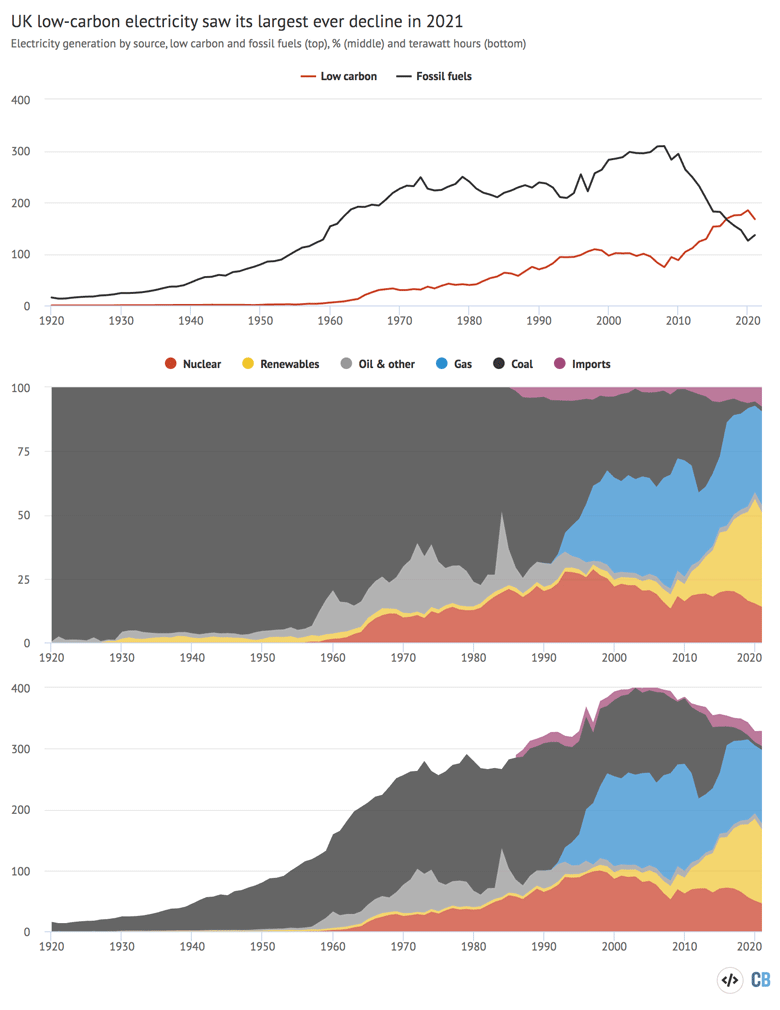
Prime: Electrical energy technology from low-carbon sources and fossil fuels, TWh. Center: Share of UK electrical energy by supply, %, 1920-2021. Backside: Technology by supply, TWh, 1920-2021. Supply: BEIS and Carbon Transient evaluation. Chart by Joe Goodman for Carbon Transient utilizing Highcharts.
Regardless of the report fall in 2021, low-carbon sources nonetheless generated greater than half of UK electrical energy (51%), because the chart above exhibits, with fossil fuels making up 39% and imports one other 8%.
Partly, this was attributable to the truth that demand barely elevated from the lockdown-induced lows seen in 2020 (backside panel).
One other contributor was two new interconnector cables – the North Sea Hyperlink with Norway and IFA2 with France – which helped increase electrical energy imports, regardless of a extended outage for the present IFA1 cross-channel cable.
The remaining 3% of the combo in 2021 was from pumped hydro storage (1%) and different sources (2%), together with the UK’s rising fleet of battery storage websites, in addition to waste incinerators.
Altering combine
The chart under exhibits a extra granular image of UK electrical energy technology since 2010, with renewables damaged down into its constituent elements.
It exhibits that elevated technology from fuel (darkish blue, up 9%) and imports (purple, up 37%) compensated for diminished low-carbon provides in 2021.
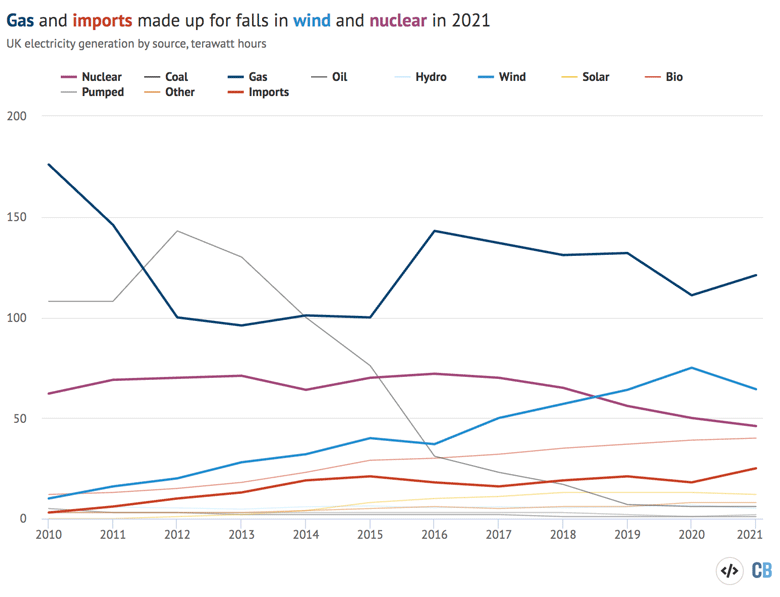
UK electrical energy technology by supply, terawatt hours, 2010-2021. Supply: BEIS and Carbon Transient evaluation. Chart by Joe Goodman for Carbon Transient utilizing Highcharts.
Notably, regardless of rising final 12 months, fuel technology remained some 8% under 2019 ranges and properly under earlier highs, at practically a 3rd decrease than output from the gas in 2010.
Equally, the 12% bump in coal technology (black) left the gas properly under its 2019 determine and nonetheless at traditionally low ranges. There have been 90 full days with out coal technology in 2021, Carbon Transient evaluation exhibits, down from 180 days in 2020, however nonetheless above 83 in 2019 and 21 in 2018.
Mixed technology from coal and fuel final 12 months, at 127TWh, was some 55% under 2010 ranges. In the meantime, imports reached their highest degree on report, at 25TWh and eight% of the combo total.
The chart additionally exhibits the stark discount in wind technology in 2021 (gentle blue) as above-average wind circumstances in 2020 gave solution to the bottom common wind speeds in a decade.
Biomass grew by 2% to account for 12% of UK electrical energy in 2021, practically a 3rd of the whole from all renewables. Some two-thirds of the biomass output is from “plant biomass”, primarily wooden pellets burnt at Lynemouth in Northumberland and the Drax plant in Yorkshire. The rest was from an array of smaller websites primarily based on landfill fuel, sewage fuel or anaerobic digestion.
The federal government’s advisory Local weather Change Committee (CCC) says the UK ought to “transfer away” from large-scale biomass energy vegetation, as soon as present subsidy contracts expire in 2027.
Utilizing biomass to generate electrical energy is not zero-carbon and in some circumstances might result in larger emissions than from fossil fuels. Furthermore, there are extra priceless makes use of for the world’s restricted provide of biomass feedstock, the CCC says, together with carbon sequestration and hard-to-abate sectors with few options.
Totally decarbonised?
The UK authorities has set an ambition to “absolutely decarbonise” the electrical energy system by 2035 as a part of its technique to achieve net-zero greenhouse fuel emissions by 2050.
This implies bringing the carbon depth of the grid – the quantity of CO2 emitted per unit of electrical energy technology – down, or at the very least very near zero.
There had been speedy and regular progress in direction of this aim over the previous decade, with eight years of successive falls in carbon depth from 486gCO2/kWh in 2012 to only 183gCO2/kWh in 2020.
Nonetheless, final 12 months’s improve in fossil fuels to compensate for the autumn in low-carbon output means the carbon depth of UK electrical energy elevated by 9% to 199gCO2/kWh, Carbon Transient estimates.
To be able to absolutely decarbonise the grid by 2035, low-carbon sources might want to change the roughly 40% of demand that’s at the moment met by fossil fuels. On the similar time, demand is anticipated to extend by round 15% by 2035 as a rising share of warmth and transport is inspired.
This problem is illustrated within the illustrative determine under, which exhibits the present make-up of UK electrical energy technology on the left and, in spherical numbers, the scenario in 2035 on the precise.
The determine exhibits that there’s a shortfall between present plans and what can be wanted to completely decarbonise the grid, even with comparatively beneficial assumptions. Any shortfall is more likely to be met by fossil fuels, breaching the federal government’s 2035 ambition.
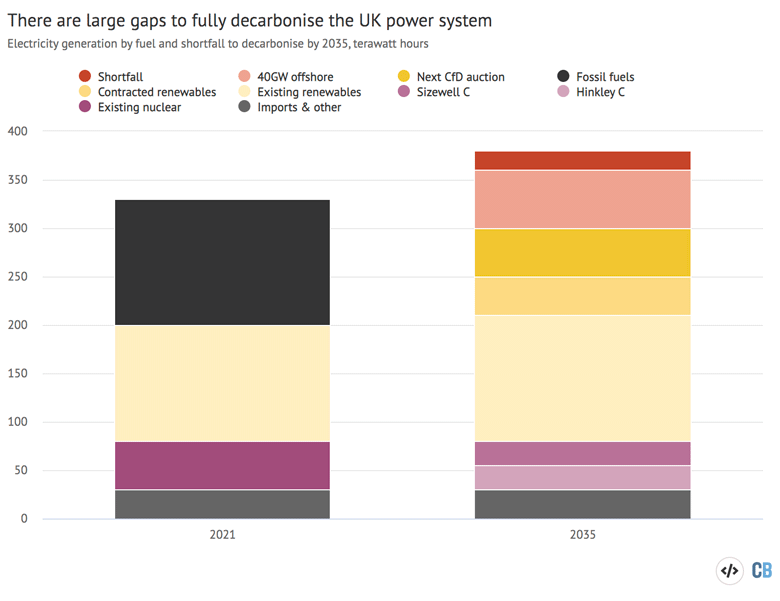
The UK electrical energy combine in 2021 (left) and 2035 (proper) damaged down by supply, in spherical numbers of terawatt hours. Supply: Carbon Transient evaluation. Chart by Joe Goodman for Carbon Transient utilizing Highcharts.
Fossil fuels, primarily fuel, provided round 40% of the UK’s electrical energy final 12 months – some 130TWh (darkish gray). To satisfy the federal government ambition, this might all want changing.
For illustrative functions, Carbon Transient has assumed that imports and different sources proceed to provide round 30TWh of electrical energy annually by 2035.
The 50TWh of low-carbon electrical energy from present nuclear energy vegetation (purple wedge, left) is about to vanish as they’re all scheduled to shut by 2035. This output might be changed by the under-construction Hinkley C and proposed Sizewell C vegetation (lighter purples, 25TWh every).
A lot of the UK’s present renewable capability – with an anticipated output of 130TWh in a mean 12 months, however nearer to 120TWh in 2021 – will nonetheless be working by 2035 (gentle yellow).
A big proportion of biomass subsidies are attributable to expire in 2027 and the oldest wind and photo voltaic farms will begin to attain the tip of their life, however, for illustrative functions, Carbon Transient has assumed that every one present renewable capability will stay operational.
Present contracts for distinction (CfDs) imply an extra 9 gigawattts (GW) of offshore wind is attributable to come on-line within the subsequent few years and can generate roughly 40TWh per 12 months (mid yellow).
The subsequent CfD public sale, which is at the moment open and can announce outcomes this summer time, is because of safe one other 12GW of capability, together with as much as 5GW of onshore renewables and 6-8GW of offshore wind. This is able to be sufficient to generate roughly 50TWh (darkish yellow).
The prime minister Boris Johnson has set a goal of 40GW of offshore wind by 2030, which means an extra 12-14GW on high of these already contracted or anticipated to win CfDs within the subsequent public sale. Reaching this goal would imply roughly one other 60TWh of low-carbon technology (pale purple).
Assuming all the above and given demand in 2035, as anticipated by the federal government, there would nonetheless be a shortfall of roughly 20TWh to completely decarbonise the grid (purple).
If a few of the UK’s present renewable capability have been to shut, if imports have been to fall or if plans and targets for brand new nuclear and offshore wind weren’t met then there can be a bigger shortfall to completely decarbonising the grid in 2035, with the chance that any hole can be stuffed by fossil fuels.
Alternatively, if utility agency EDF wins approval to lengthen the life of the 1.2GW Sizewell B nuclear plant past 2035, because it hopes to do, then this might assist shut the shortfall in low-carbon output.
Methodology
The figures within the article are from Carbon Transient evaluation of information from BEIS Vitality Traits chapter 5 and chapter 6, in addition to from BM Stories. The figures from BM Stories are for electrical energy provided to the grid in Nice Britain solely and are adjusted to incorporate Northern Eire.
In Carbon Transient’s evaluation, the BM Stories numbers are additionally adjusted to account for electrical energy utilized by energy vegetation on website and for technology by vegetation not related to the high-voltage nationwide grid. This consists of many onshore windfarms, in addition to industrial fuel mixed warmth and energy vegetation and people burning landfill fuel, waste or sewage fuel.
The evaluation of carbon depth relies on the methodology printed by Nationwide Grid ESO.
BEIS historic electrical energy knowledge, together with years earlier than 2009, is adjusted to replicate on-site technology and mixed with knowledge on imports from a separate BEIS dataset.
The Instances, Observer and Each day Categorical reported preliminary outcomes from this similar evaluation.
Sharelines from this story