The UK’s greenhouse gasoline emissions fell by 5.7% in 2023 to their lowest degree since 1879, in line with new Carbon Transient evaluation.
The final time UK emissions had been this low, Queen Victoria was on the throne, Benjamin Disraeli was prime minister, Mosley Avenue in Newcastle grew to become the first highway on the planet with electrical lighting and 59 individuals died within the Tay Bridge catastrophe in Dundee.
Carbon Transient’s evaluation, primarily based on preliminary authorities power knowledge, exhibits emissions fell to only 383m tonnes of carbon dioxide equal (MtCO2e) in 2023. That is the primary time they’ve dropped under 400MtCO2e since Victorian occasions.
Different key findings from the evaluation embody:
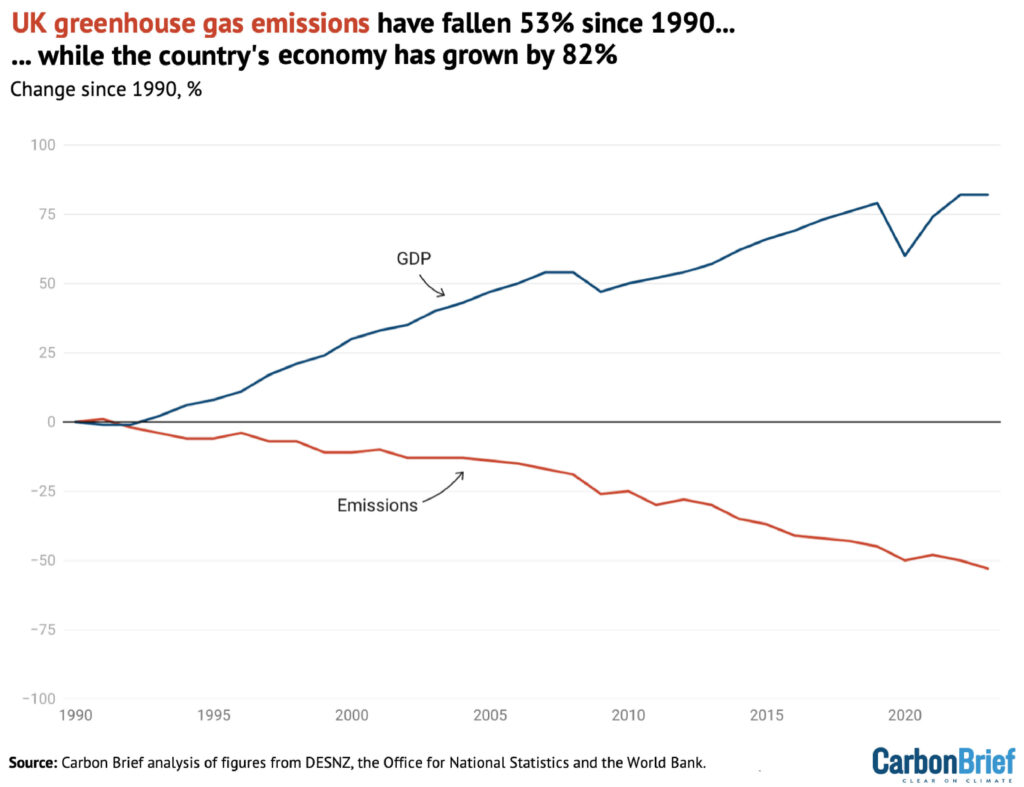
- The UK’s emissions are actually 53% under 1990 ranges, whereas GDP has grown by 82%.
- The drop in emissions in 2023 was largely resulting from an 11% fall in gasoline demand. This was resulting from greater electrical energy imports after the French nuclear fleet recovered, above-average temperatures and weak underlying demand pushed by excessive costs.
- Gasoline demand would have fallen even quicker, however for a 15% fall in UK nuclear output.
- Coal use fell by 23% in 2023 to its lowest degree for the reason that 1730s, as all however one of many UK’s remaining coal-fired energy stations closed down.
- Transport was the single-largest sector when it comes to emissions, adopted by buildings trade, agriculture and electrical energy technology. The electrical energy sector seemingly dropped under agriculture for the primary time.
Whereas the 23MtCO2e discount in 2023 was quicker than the 14MtCO2e per yr common wanted to succeed in net-zero by 2050, it was principally unrelated to deliberate local weather motion. The UK might want to deal with emissions from buildings, transport, trade and agriculture to succeed in its 2050 goal.
The evaluation is the most recent in a long-running collection of annual estimates from Carbon Transient, masking emissions throughout 2022, 2020, 2019, 2018, 2017, 2016, 2015 and 2014.
Replace 28/3/2024: Official provisional authorities estimates put the drop in UK greenhouse gasoline emissions in 2023 at 5.4%, in contrast with Carbon Transient’s 5.7%. The federal government stated emissions fell to 384MtCO2e in 2023, similar to Carbon Transient’s 383MtCO2e.
Lowest since 1879
The UK’s territorial greenhouse gasoline emissions – people who happen inside the nation’s borders – have now fallen in 25 of the 34 years since 1990.
(Consumption-based emissions, together with CO2 embedded in imported items and providers, had been growing till 2007, however have since fallen at an analogous fee to territorial emissions.)
Aside from transient rebounds after the worldwide monetary disaster and the Covid-19 lockdowns, UK emissions have fallen throughout yearly for the previous 20 years.
The newest 23MtCO2e (5.7%) discount in 2023 takes UK emissions right down to 383MtCO2e, in line with Carbon Transient’s new evaluation.
That is the bottom since 1879 – exterior the 1926 basic strike – as proven within the determine under.
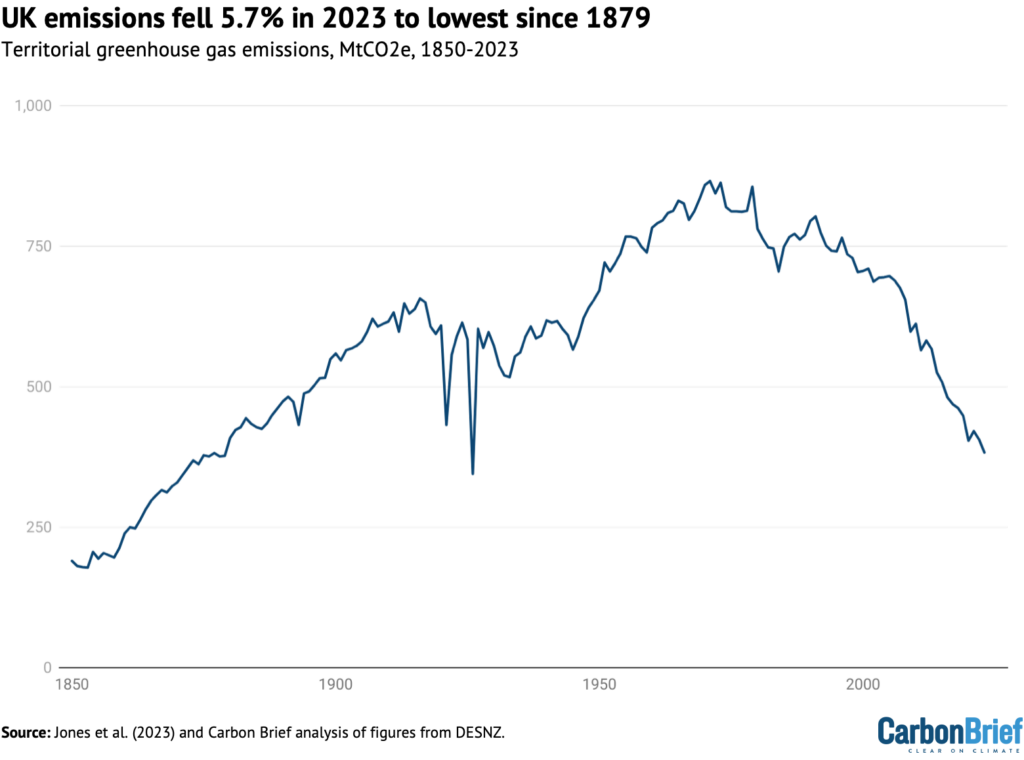
Having dropped to a then-record low for the trendy period of 404MtCO2e in the course of the top of Covid in 2020, UK emissions bounced again in 2021 because the financial system reopened.
Whereas emissions declined in 2022, they remained above 2020 ranges. In 2023, nevertheless, emissions fell under the lows seen throughout Covid lockdowns, to ranges not seen since Victorian occasions.
Unintentional motion
The most important contributor to the drop in UK greenhouse gasoline emissions in 2023 was an 11% discount in gasoline demand, which accounted for round two-thirds of final yr’s total decline. This took the UK’s gasoline demand to its lowest degree for the reason that Nineteen Eighties.
Nonetheless, the drop in 2023 was not primarily resulting from deliberate local weather motion.
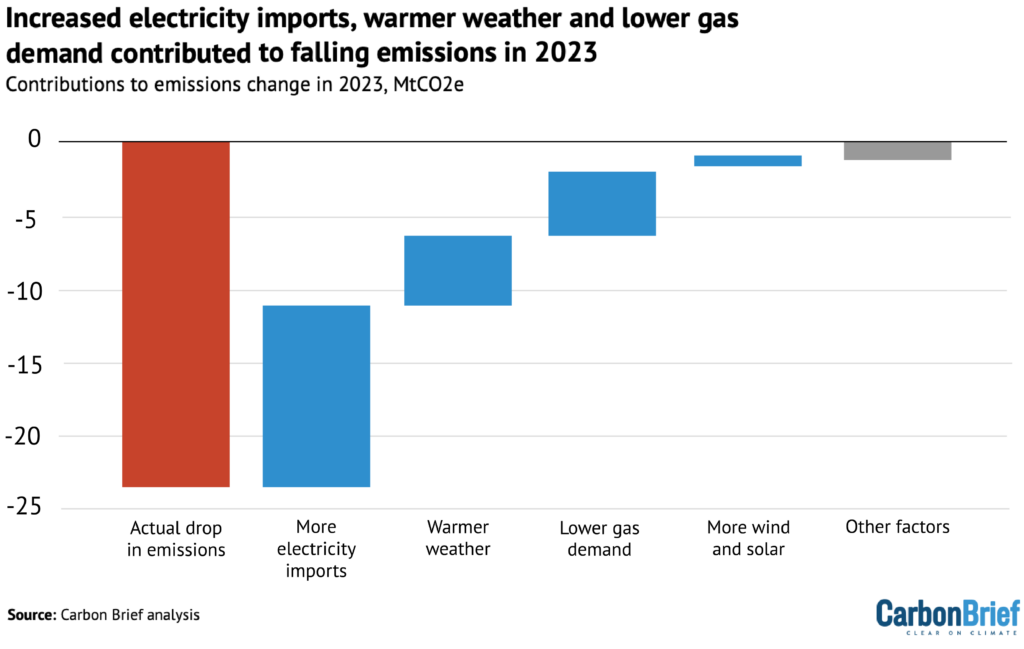
The determine under exhibits the estimated precise drop in emissions in pink, adopted by contributions from a collection of things that decreased emissions, in blue, and different elements in gray.
Essentially the most vital issue was the UK returning to its long-term place as a internet electrical energy importer in 2023, decreasing demand for domestically generated energy from gasoline by greater than 20%.
This adopted an anomalous yr in 2022, when the UK was a internet exporter for the first time ever, on account of widespread outages within the French nuclear fleet.
Decrease demand for gasoline energy accounted for greater than two-thirds of the autumn in gasoline use total.
Subsequent, above-average temperatures decreased the necessity for heating, whereas persevering with very excessive costs since Russia’s invasion of Ukraine brought about weak underlying demand for gasoline.
Reflecting each of those elements, there was a 6% drop in home demand in 2023, accounting for a fifth of the general decline in gasoline consumption. The same 7% drop in business demand for gasoline accounted for an additional tenth of the entire, with a 5% drop in industrial demand the rest.
Lastly, the determine exhibits that there was a small discount in gasoline demand and related CO2 emissions on account of elevated wind and photo voltaic technology.
The impression of rising wind and photo voltaic capability in 2023 was muted by common windspeeds being under common and the common variety of solar hours falling sharply in contrast with 2022.
The UK’s emissions would have fallen even additional in 2023 if not for a 15% decline within the output of the nation’s nuclear fleet. This adopted the closure in 2022, of the Hunterston B station in Scotland and the Hinkley Level B plant in Somerset, in addition to upkeep outages.
The decline in 2023 means UK nuclear output fell to the bottom degree for the reason that early Nineteen Eighties. Following the positioning closures in 2022, the UK solely has 5 operational nuclear energy crops remaining, all however one in every of which – Sizewell B in Suffolk – are resulting from shut this decade.
Out of coal
After gasoline, the next-largest driver of falling UK emissions in 2023 was coal, accounting for round 14% of the general drop in emissions.
The decline of coal use within the UK – for houses, railways, factories and energy stations – is a significant a part of the long-term discount in greenhouse gasoline emissions over the previous 30 years.
Components on this long-term decline embody controls on home coal burning to restrict air air pollution, the tip of steam railways, the shift from coal-based “city gasoline” to “pure” gasoline from the North Sea, the deindustrialisation of the Seventies and the “sprint for gasoline” of the Nineties.
Extra just lately, coal demand has dropped precipitously because the speedy build-out of renewable sources of electrical energy has mixed with falling demand and carbon pricing that favours gasoline.
The determine under exhibits how UK coal demand surged in the course of the industrial revolution earlier than levelling off via the twentieth century, barring basic strikes in 1921 and 1926.
Coal demand has been falling steadily for the reason that passage of the Clear Air Act in 1956, in response to London’s “nice smog” of 1952. In 2023, UK coal demand fell by one other 23% to the bottom degree for the reason that 1730s, when George II was on the throne and Robert Walpole was prime minister.
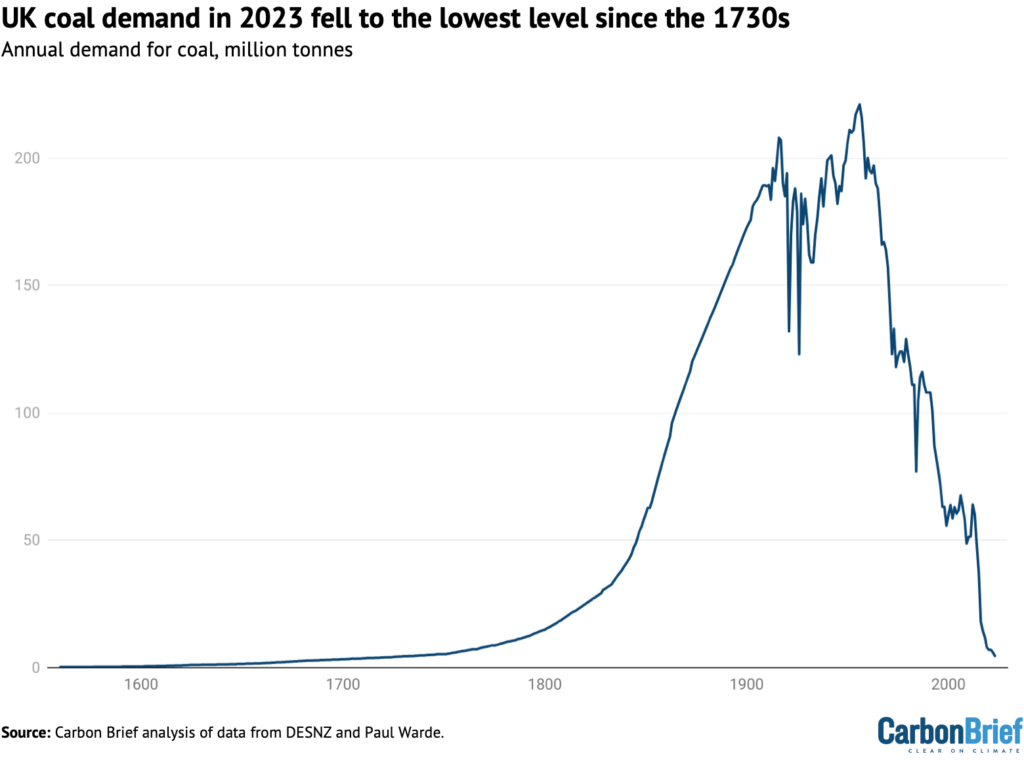
The current discount of coal demand is essentially right down to the demise of coal energy, which made up round 40% of the UK’s electrical energy technology as just lately as 2012. Coal energy output has fallen by 97% over the previous decade, accounting for 87% of the autumn in UK coal demand total.
In 2023, just one% of the UK’s electrical energy got here from coal, with three coal-fired crops closing down: the coal models at Drax in Yorkshire; Kilroot in Northern Eire; and West Burton A in Lincolnshire.
As of the beginning of October 2023, just one coal plant stays – the Ratcliffe-on-Soar web site in Nottinghamshire. Operator Uniper plans to shut Ratcliffe in September 2024, forward of the federal government’s deadline to finish coal energy by October 2024.
Sectoral shifts
The reductions in gasoline use for energy and constructing warmth, in addition to the autumn in coal use for energy, additional cemented the transport sector as the biggest contributor to UK emissions in 2023.
That is proven within the determine under, which highlights how transport emissions have barely modified over the previous a number of many years as extra environment friendly vehicles have been offset by elevated visitors.
The facility sector was the biggest contributor to the UK’s emissions till 2014. In 2023, it was seemingly solely the fifth-largest under transport, buildings, trade and – for the primary time – additionally agriculture.
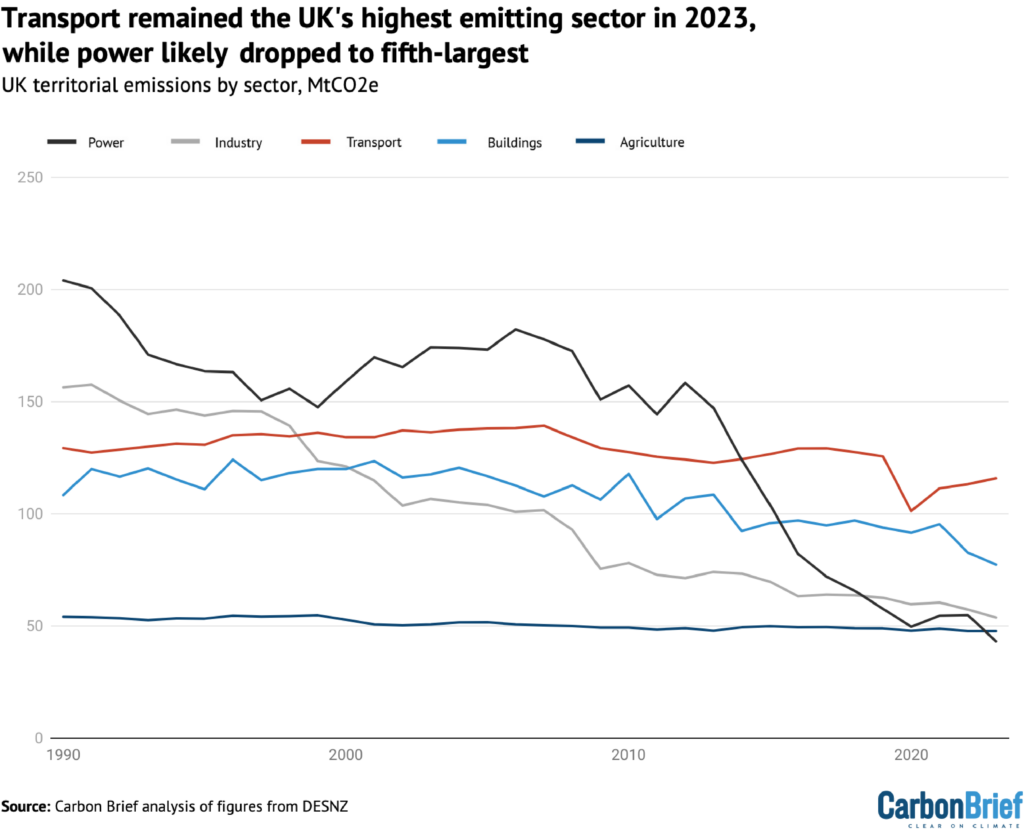
As of 2023, transport emissions had been solely round 10% under 1990 ranges and made up practically a 3rd of the UK’s total whole. There are actually greater than 1,000,000 electrical autos (EVs) on the UK’s highway, which could have prevented round 2MtCO2e of annual emissions.
Nonetheless, the federal government has additionally frozen or reduce gasoline obligation yearly since 2010, fairly than growing it in step with inflation, including as much as round 20MtCO2e to the UK’s whole.
Emissions from buildings – mainly for heating and cooling – are the second-largest contributor to the UK’s emissions, accounting for round a fifth of the entire.
They had been round one-third decrease than 1990 ranges in 2023, with improved insulation and boiler rules making the UK’s buildings extra environment friendly to warmth.
Effectivity enhancements dried up round a decade in the past and the autumn in constructing emissions since 2021 has been pushed by excessive costs suppressing demand, fairly than deliberate coverage selections.
Industrial emissions made up an estimated tenth of the UK’s whole in 2023, having fallen by two-thirds since 1990 and by 1 / 4 up to now decade.
In widespread with many different developed economies, the UK shifted from heavy trade in the direction of superior manufacturing and providers from the Seventies onwards. Nonetheless, industrial power effectivity enhancements and a shift to lower-carbon fuels are additionally a part of the image.
Agricultural emissions have barely modified for many years, making up simply over a tenth of the UK’s whole in 2023 and having fallen simply 12% since 1990 as livestock herds have shrunk.
There was a small lower in farm emissions in 2022 because the power disaster filtered via into surging costs for fertilisers. For the determine above, Carbon Transient assumes the decreased fertiliser use in 2022 continued in 2023, as fertiliser costs solely eased in summer time 2023.
Decoupling emissions
The drop in UK emissions in 2023 got here because the financial system flatlined, rising by simply 0.4% on 2022 ranges. The UK’s emissions are actually 53% under 1990 ranges whereas the financial system has grown 82%.
This “decoupling” of emissions from financial development is proven within the determine under. As famous above, this evaluation relies on territorial emissions inside the UK’s borders.
Consumption-based emissions together with imported items and providers had been climbing within the early a part of this century. Nonetheless, emissions cuts over the previous 20 years have been very largely pushed by sectors that can’t simply be “outsourced”, notably energy and constructing warmth.
The UK is now in a gentle recession and the financial system is just anticipated to develop by round 1% in 2024. Current tendencies within the “emissions depth” of the UK financial system – the emissions per unit of GDP – and weak financial development means that emissions might proceed to fall in 2024.
Alternatively, gasoline and oil costs are easing to pre-crisis ranges, whereas above-average temperatures might not proceed for an additional yr. Petrol demand rose by practically 5% in 2023 as visitors continued to rebound from the pandemic – and jet gasoline use equally climbed by 16%.
Furthermore, the one-off impression of the UK returning to internet electrical energy imports has now unwound. As such, additional emissions cuts in 2024 are removed from assured.
Goal practise
Whereas the UK has made speedy progress in slicing its territorial emissions since 1990, it stays solely round midway to reaching its net-zero goal for 2050, because the chart determine exhibits.
Emissions fell by 23MtCO2e in 2023, in line with Carbon Transient’s evaluation. That is quicker than the 14MtCO2e discount wanted yearly for the following quarter-century to succeed in net-zero by 2050.
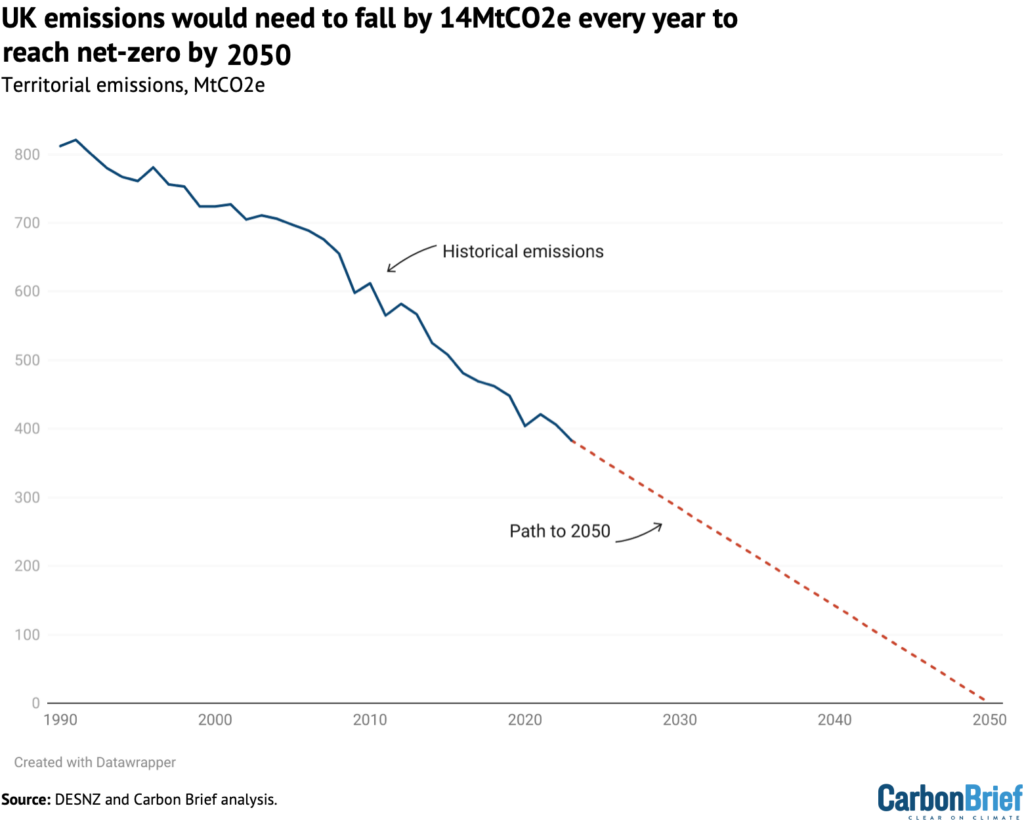
Nonetheless, with just one coal-fired energy station remaining and the facility sector total now seemingly solely the fifth-largest contributor to UK emissions, the nation might want to begin slicing into gasoline energy and trying to different sectors, whether it is to proceed making progress in the direction of its targets.
This can imply increasing wind and photo voltaic capability to cut back gasoline use, whereas retaining gas-fired energy stations for durations of low wind and beginning to construct low-carbon options, corresponding to gasoline with carbon seize and storage, long-term power storage or hydrogen-fired generators.
Emissions from highway transport and buildings shall be key areas if the UK is to progress, which is why adjustments to authorities plans round electrical autos and warmth pumps might be problematic.
Equally, a authorities resolution to “carry ahead” the “surplus” emissions cuts from earlier years – largely resulting from exterior occasions corresponding to Covid – would severely weaken UK targets at a time when continued ambition is required, to remain on monitor for medium- and long-term local weather targets.
Methodology
The place to begin for Carbon Transient’s evaluation of UK greenhouse gasoline emissions is preliminary authorities estimates of power use by gasoline. These are revealed quarterly, with the ultimate quarter of every yr showing in figures revealed on the finish of the next February. The identical strategy has precisely estimated year-to-year adjustments in emissions in earlier years (see desk, under).
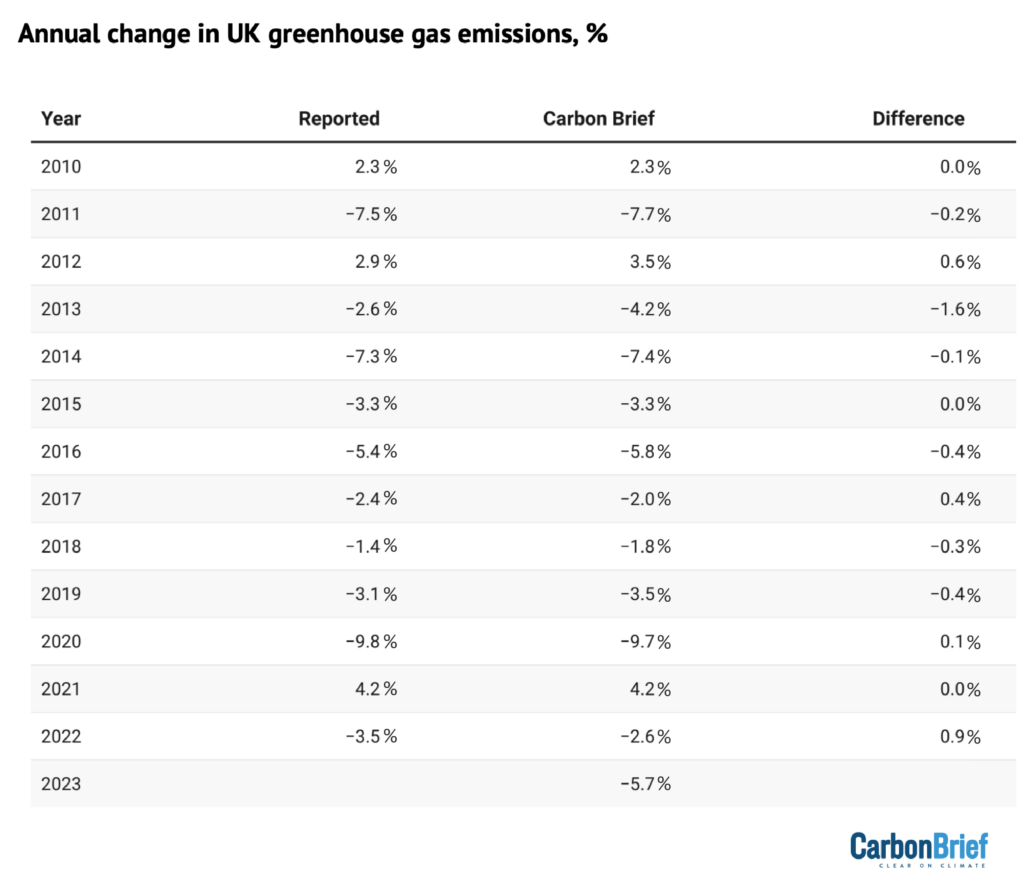
One giant supply of uncertainty is the provisional power use knowledge, which is revised on the finish of March every year and sometimes once more in a while. Emissions knowledge can also be topic to revision in gentle of enhancements in knowledge assortment and the methodology used, with main revisions in 2021.
The desk above applies Carbon Transient’s emissions calculations to the comparable power use and emissions figures, which can differ from these revealed beforehand.
One other supply of uncertainty is the truth that Carbon Transient’s strategy to estimating the annual change in emissions differs from the methodology used for the federal government’s personal provisional estimates. The federal government has entry to extra granular knowledge not accessible for public use.
Carbon Transient’s evaluation takes figures on the quantity of power sourced from coal, oil and gasoline reported in Vitality Tendencies 1.2. These figures are mixed with conversion elements for the CO2 emissions per unit of power, revealed yearly by the UK authorities. Conversion elements can be found for every gasoline kind, for instance, petrol, diesel, gasoline, coal for electrical energy technology.
For oil, the evaluation additionally attracts on Vitality Tendencies 3.13, which additional breaks down demand in line with the subtype of oil, for instance, petrol, jet gasoline and so forth. Equally, for coal, the evaluation attracts on Vitality Tendencies 2.6, which breaks down strong gasoline use by subtype.
Emissions from every gasoline are then estimated from the power use multiplied by the conversion issue, weighted by the relative proportions for every gasoline subtype.
For instance, the UK makes use of roughly 50m tonnes of oil equal (Mtoe) within the type of oil merchandise, round half of which is from highway diesel. So half the entire power use from oil is mixed with the conversion issue for highway diesel, one other one-fifth for petrol and so forth.
Vitality use from every fossil gasoline subtype is mapped onto the suitable emissions conversion issue. In some instances, there isn’t any direct read-across, during which case the closest acceptable substitute is used. For instance, power use listed as “bitumen” is mapped to “processed gasoline oils – residual oil”. Equally, strong gasoline utilized by “different conversion industries” is mapped to “petroleum coke”, and “different” strong gasoline use is mapped to “coal (home)”.
The power use figures are calculated on an inland consumption foundation, which means they embody bunkers consumed within the UK for worldwide transport by air and sea. In distinction, nationwide emissions inventories exclude worldwide aviation and transport.
The evaluation, subsequently, estimates and removes the a part of oil use that’s as a result of UK’s share of worldwide aviation. It attracts on the UK’s last greenhouse gasoline emissions stock, which breaks emissions down by sector and studies the entire for home aviation.
This home emissions determine is in contrast with the estimated emissions resulting from jet gasoline use total, primarily based on the suitable conversion issue. The evaluation assumes that home aviation’s share of emissions is equal to its share of jet gasoline power use.
Along with estimating CO2 emissions from fossil gasoline use, Carbon Transient assumes that CO2 emissions from non-fuel sources, corresponding to land-use change and forestry, are the identical as a yr earlier. Remaining greenhouse gasoline emissions are assumed to vary in step with the most recent authorities power and emissions projections.
These assumptions are primarily based on the UK authorities’s personal methodology for preliminary greenhouse gasoline emissions estimates, revealed in 2019.
Word that the figures on this article are for emissions inside the UK measured in line with worldwide pointers. This implies they exclude emissions related to imported items, together with imported biomass, in addition to the UK’s share of worldwide aviation and transport.
The Workplace for Nationwide Statistics (ONS) has revealed detailed comparisons between numerous totally different approaches to calculating UK emissions, on a territorial, consumption, environmental accounts or worldwide accounting foundation.
The UK’s consumption-based CO2 emissions elevated between 1990 and 2007. Since then, nevertheless, they’ve fallen by an analogous variety of tonnes as emissions inside the UK.
Bioenergy is a big supply of renewable power within the UK and its local weather advantages are disputed. Opposite to public notion, nevertheless, solely round one quarter of bioenergy is imported.
Worldwide aviation is taken into account a part of the UK’s carbon budgets and faces the prospect of tighter limits on its CO2 emissions. The worldwide transport sector has a goal to a minimum of halve its emissions by 2050, relative to 2008 ranges.
Sharelines from this story
