“Fragmented governance” between biodiversity, native climate change, meals, water and effectively being is putting all of those strategies at risk, consistent with a severe new report from the Intergovernmental Science-Protection Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Corporations (IPBES).
The report, usually referred to as the “nexus analysis”, explores the interlinkages between native climate change, biodiversity, meals, water and human effectively being.
It says that specializing in a single part of the nexus on the expense of the others might have detrimental impacts for every individuals and the planet.
On the an identical time, many of the actions that could be taken to cope with nature loss might have co-benefits for the native climate.
The report moreover finds that funding for nature is dwarfed by every non-public and non-private finance that goes in route of nature-harming actions.
Nonetheless, it says, reforming worldwide financial strategies would possibly help deal with the “funding gap” wished to efficiently defend nature.
These conclusions sort part of a “summary for policymakers”, a 57-page doc that explains the vital factor messages of the report. The overall report is perhaps revealed sometime subsequent yr.
IPBES is an neutral physique that provides scientific suggestion spherical biodiversity and biodiversity loss to policymakers, along with by the use of the Convention on Natural Selection. It was modelled after the Intergovernmental Panel on Native climate Change and capabilities in quite a bit the an identical strategy.
Prof Pam McElwee, co-chair of the report and a professor at Rutgers School, knowledgeable a press briefing that biodiversity, native climate, meals, water and effectively being should not be dealt with as “single-issue crises”. She added:
“These are interlinked crises. They’re compounding each other. They’re making points worse, and the current enterprise as frequent technique is simply not solely failing to cope with the drivers of these points, [but] in some situations, we’re dropping money on account of we’re duplicating insurance coverage insurance policies, when in fact, we may probably be treating them as factors that should be dealt with collectively.”
Proper right here, Carbon Transient explains 5 key takeaways from the IPBES “nexus” analysis report.
- Biodiversity loss locations meals and water strategies, human effectively being and the native climate at risk
- Focusing solely on meals security leads to ‘excessive trade-offs’ with native climate, water and biodiversity
- Shifting to sustainable healthful diets will revenue of us and the planet
- All obtainable decisions for restoring nature would moreover help to cope with and adapt to native climate change
- Reforming worldwide financial strategies can also assist shut the biodiversity funding gap
1. Biodiversity loss locations meals and water strategies, human effectively being and the native climate at risk
The report explores how the decline of biodiversity in “all areas of the world” has extreme penalties for meals, water, effectively being and native climate change.
It stresses that biodiversity is “vital” to human existence, on account of it helps water and meals supplies, underpins public effectively being and contributes to the soundness of the native climate.
Nonetheless over the previous 30-50 years, biodiversity has declined by a median of 2-6% each decade all through “all of the assessed indicators”, consistent with the report.
It notes that the persevering with decline has been attributable to an intensification of the direct drivers of biodiversity loss: land- and sea-use change, native climate change, overexploitation of property, invasive alien species and air air pollution.
These tendencies have, in flip, been attributable to “a wide range of indirect drivers”, along with monetary, demographic, cultural and technological changes, the report argues.
When these “direct” and “indirect” drivers of biodiversity loss work along with each other, they set off “cascading impacts among the many many nexus components”, the report warns. Significantly, it notes that native climate change and biodiversity loss “work collectively and compound each other to negatively impression ecosystem resilience and all the alternative nexus components”.
The doc components to “fragmented governance” of biodiversity, water, meals, effectively being and native climate change as a severe obstacle stopping environment friendly movement on the issues.
Whereas environmental legal guidelines have been “partially worthwhile”, they’re “unlikely to be completely environment friendly with out further concerted efforts to cope with interlinkages among the many many nexus components and their direct and indirect drivers”, it warns.
Prof Paula Harrison, co-chair of the report and a scientist on the UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology, says that governance strategies should replicate the interconnections between biodiversity, meals, effectively being, water and native climate change. She knowledgeable a press briefing on 16 December:
“Because of our current governance strategies are typically utterly completely different departments, they’re working in silos. They’re very fragmented, they usually’re working and rising protection in isolation – often these hyperlinks [between climate, health, biodiversity, water and food] won’t be even acknowledged or ignored.
“What that actually means is that you’d be capable to merely get unintended penalties or trade-offs that emerge on account of of us merely weren’t contemplating throughout the holistic strategy.”
For example, unsustainable agricultural practices launched to increase meals manufacturing finish in biodiversity loss, unsustainable water utilization, lowered meals vary and top quality, and elevated air air pollution and greenhouse gasoline emissions, the report says.
The graphic beneath affords an illustration of how unsustainable agriculture can impression all 5 of the nexus components.
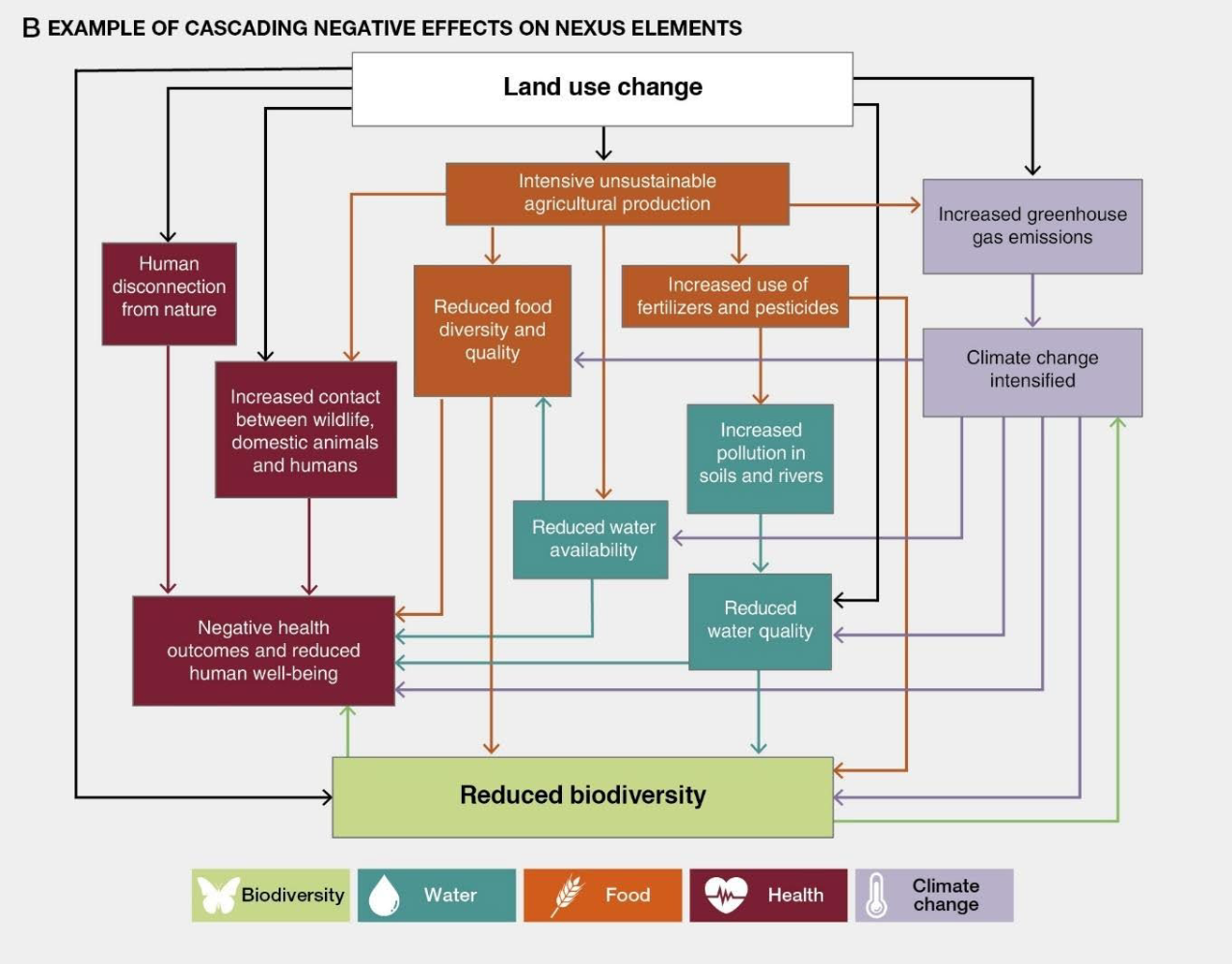
Moreover, the report finds that over the previous 50 years, decision makers have prioritised “short-term benefits and financial returns for a small number of of us”, whereas ignoring the detrimental impacts of their actions on the 5 nexus components.
This oversight exacerbates societal inequalities, consistent with the report, provided that communities in rising worldwide places and Indigenous peoples are disproportionately affected by biodiversity loss, water and meals insecurity, native climate change and effectively being risks.
Basic, it says that “dominant monetary strategies” are inflicting “unsustainable and inequitable monetary progress”, noting that $7tn a yr is invested in actions detrimental to nexus components.
2. Focusing solely on meals security leads to ‘excessive trade-offs’ with native climate, water and biodiversity
To judge how the 5 nexus components – biodiversity, water, meals, effectively being and native climate – will work along with each other over the twenty first century, the authors used 186 conditions from 52 analysis to develop six “nexus state of affairs archetypes”.
The desk beneath reveals the overall projected impression on each nexus part beneath the utterly completely different archetypes. The graphic beneath reveals how the utterly completely different nexus components impression each other beneath each archetype.
In every graphics, blue arrows current a constructive impression, crimson a detrimental impression and grey a variable impression. Additional arrows, or thicker strains, level out a stronger impression.
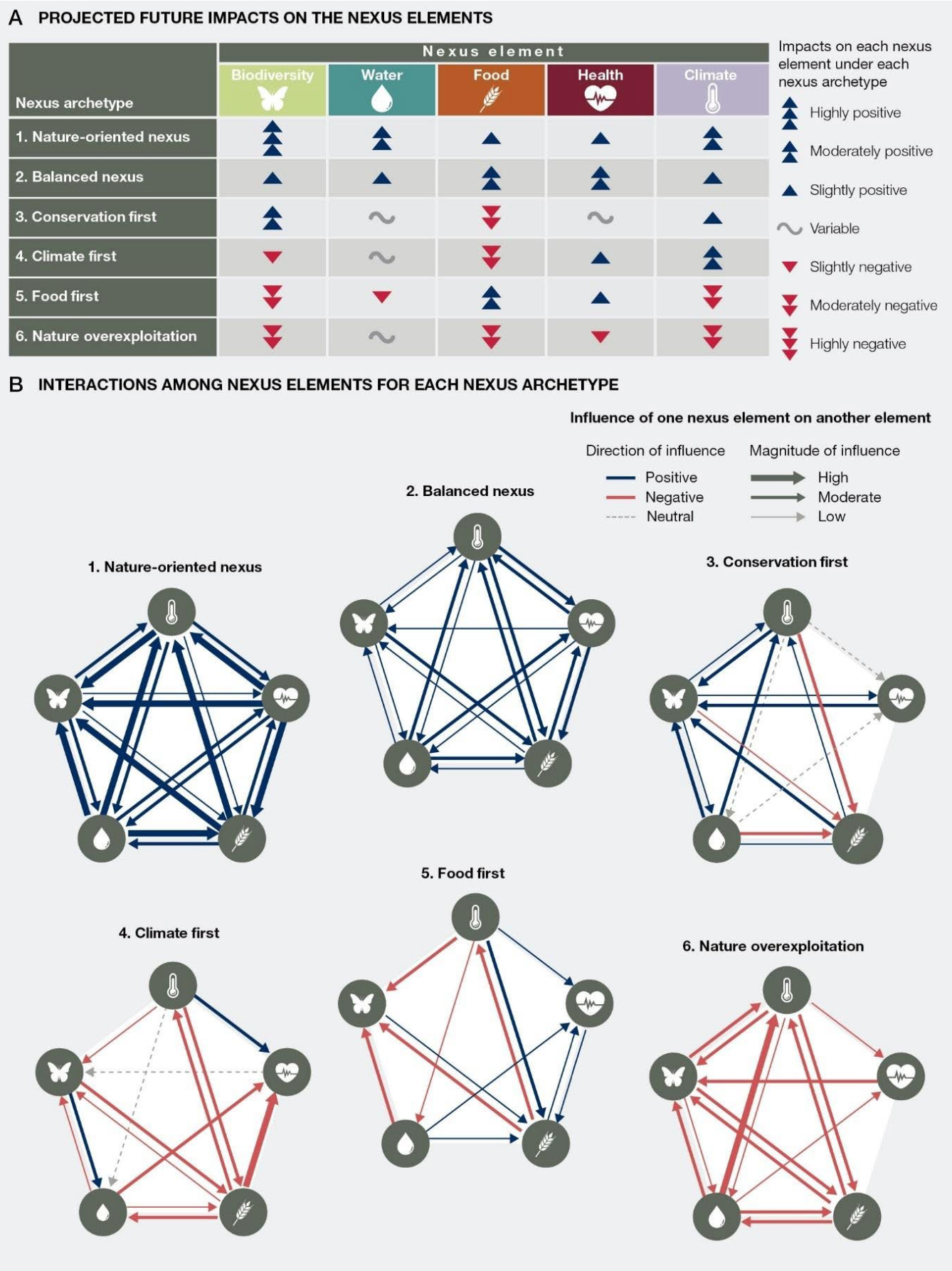
The report calls archetypes one and two “sustainability conditions”.
These are associated to sustainable consumption and manufacturing, healthful diets, lowered meals waste and reduce water use. These archetypes endeavor constructive long-term outcomes all through all of the nexus components.
Furthermore, the benefits of monetary progress are further evenly distributed all through utterly completely different “societal groups”, and quite a lot of actors and knowledge strategies – along with Indigenous knowledge – are involved in decision-making.
The “nature-oriented nexus” – the first archetype – focuses on rising protected areas and enhancing their effectiveness, with a cope with areas with extreme biodiversity. This takes “deliberate efforts to cope with current and rising injustices and inequality”.
The report finds proof that “defending as a lot as 30% of terrestrial, freshwater and marine areas can current nexus-wide benefits, if these are efficiently managed for nature and different individuals”.
The archetype moreover sees a metamorphosis of world meals strategies, by the use of changes along with elevated sustainable agricultural practices, reducing meals waste, rising new meals sources and promoting healthful, sustainable diets.
Archetype two, known as the “balanced nexus”, is characterised by stronger environmental regulation and fewer reliance on utilized sciences than the nature-oriented nexus. This archetype has a strong cope with restoration and sustainable use of pure property. It has fewer constructive impacts on biodiversity, water and native climate and barely further constructive impacts for meals and human effectively being, as compared with archetype one.
Within the meantime, archetypes three, 4 and 5 each prioritise a selected nexus part. These archetypes drive “excessive trade-offs among the many many nexus components” and finish in “unsustainable and inequitable monetary progress”.
For example, archetype 5 – “meals first” – makes use of “unsustainable” agricultural processes, which finish in bigger greenhouse gasoline emissions, land-use change, water use and nitrate air air pollution. This example sees dietary effectively being improve, nonetheless has detrimental impacts on biodiversity, water and native climate change.
Archetypes 5 and 6 are “business-as-usual” conditions, which symbolize the continuation of current tendencies. These are characterised by “intensive…supplies and vitality consumption, elevated greenhouse gasoline emissions, intensive land use and unsustainable exploitation of pure property”.
The sixth archetype is named “nature overexploitation” and is characterised by detrimental impacts all through all 5 nexus components. This archetype sees overconsumption of pure property, unsustainable vitality demand and “weak environmental regulation exacerbated by delayed movement”.
The report warns that these business-as-usual conditions finish in “declining outcomes for biodiversity, primarily pushed by unsustainable meals manufacturing and helpful useful resource extraction along with native climate change”.
The report concludes:
“Maximising all nexus components concurrently is unlikely to be potential, nonetheless reaching stability all through protection targets will seemingly end in useful outcomes for nature and different individuals.”
3. Shifting to sustainable healthful diets will revenue of us and the planet
The report says it is successfully established by scientists that shifting to sustainable healthful diets and reducing meals waste would “revenue meals security and effectively being” and “in the reduction of greenhouse gasoline emissions”.
This shift would possibly moreover “unencumber land, providing in a ramification of situations co-benefits for nexus components, just like biodiversity conservation and carbon sinks”, the report says.
The analysis examines 71 “response decisions” for tackling on the very least one part of the nexus between biodiversity, water, meals security, effectively being and native climate change.
The report says that these responses “won’t be meant to be an exhaustive report”, nonetheless “symbolize a menu of decisions that could be utilized in quite a few contexts”, together with:
“Some response decisions might be not acceptable in all worldwide places, and all may very well be carried out in accordance with nationwide legal guidelines and sovereignty and in accordance with associated worldwide obligations. Even inside worldwide places, effectiveness and acceptability rely critically on political, social and ecological context.”
The graphic beneath summarises the response decisions, which can be grouped into 10 courses. The coloured tags level out which part of the nexus the selection addresses.
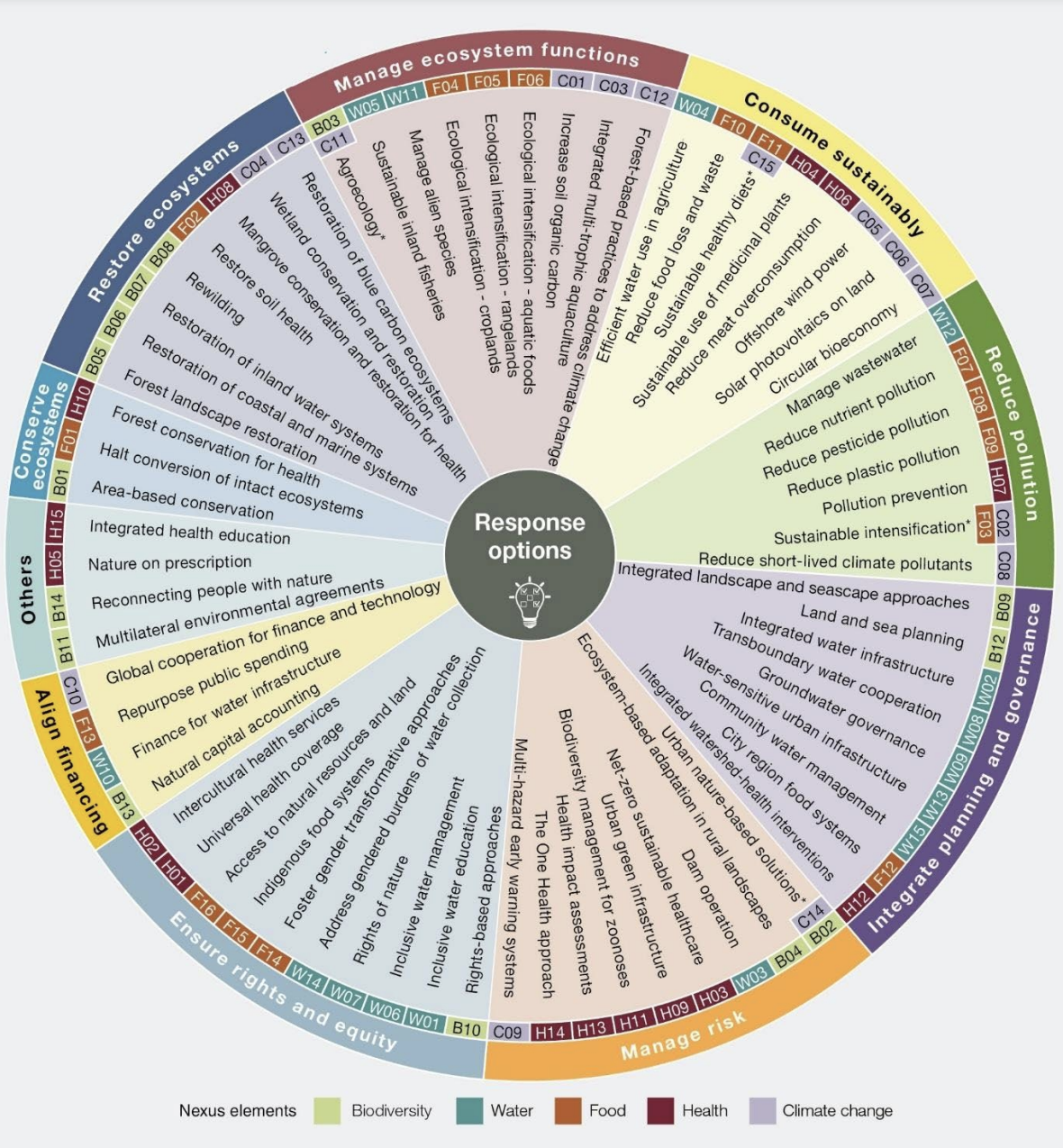
The graphic illustrates how most of the decisions for addressing meals security comprise consuming sustainably, managing ecosystem capabilities and ensuring Indigenous rights and equity.
Measures to devour sustainably in order to boost meals security embrace shifting to sustainable healthful diets and reducing meals waste.
The diagram moreover notes that human effectively being may probably be improved by reducing meat overconsumption.
The report says it is successfully established that “behaviour change is perhaps important to shift consumption practices”.
It says this can be enabled by the “rising accessibility and desirability” of sustainable healthful diets. It moreover says that implementing food-based dietary tricks to most people, “notably concentrating on public school feeding programmes”, can create a “structured demand” for healthful and sustainable meals.
This measure would possibly moreover “improve alternate options for on-farm diversification aimed towards rising present and consumption of native seasonal meals”, the report says.
The report moreover says that enhancing the sustainable use and administration of ecosystems is “notably very important for the agricultural sector”.
It is as a result of “the way in which during which meals is produced, what meals are produced and consumed, the place they’re produced, and the way in which quite a bit meals is misplaced and wasted impression every nature and different individuals”. It says the “ecological intensification” of croplands, rangelands and aquaculture can also assist to cope with meals security whereas having benefits for people and nature.
“Ecological intensification” refers again to the idea of using pure capabilities of an ecosystem to provide further meals in a sustainable strategy – as an example, by allowing wild bugs to pollinate crops.
The report moreover says “agroecology” may need constructive outcomes for biodiversity and addressing native climate change. It says:
“Agroecology represents a shift to manufacturing strategies the place equitable entry to land and a mixture of scientific and Indigenous and native knowledge data the sustainable administration of biodiversity, crops and completely different property.”
4. All obtainable decisions for restoring nature would moreover help to cope with and adapt to native climate change
Your entire obtainable decisions for restoring biodiversity examined by the report would come with co-benefits for tackling and adapting to native climate change, although the dimensions of this constructive impression varies with each technique.
The decide beneath reveals the constructive (darkish blue) and detrimental (crimson) impacts associated to the report’s 71 “response decisions” for tackling on the very least one part of the nexus between biodiversity, meals security, effectively being and native climate change (see earlier half for further on these decisions).
Inside the decide, constructive and detrimental impacts are confirmed for biodiversity (butterfly icon), water (droplet), meals security (wheat), effectively being (coronary coronary heart) and native climate change (thermometer). The size of the circle represents the relative measurement of the influence.

The decide reveals that every one the alternatives for addressing biodiversity loss (B01-14) embody a constructive impression on efforts to cope with and adapt to native climate change.
Furthermore, the report says, implementing quite a lot of response decisions collectively can have a synergistic influence, “enhanc[ing] nexus-wide benefits”. Current approaches, it supplies, “have did not harness the entire potential…on account of they have been designed and carried out in isolation”.
The report says it is successfully established that addressing nature loss by defending pure ecosystems from extra destruction would possibly embody benefits for all components of the nexus, together with:
“Conserving or halting conversion of forests and completely different ecosystems protects human effectively being and wellbeing by combating native climate change, reducing the impression of utmost local weather events, just like storms, droughts and landslides, rising water and air top quality and reducing sickness risk.”
It is also successfully established that restoring degraded ecosystems can also assist to cope with native climate change “when it targets carbon storage in forests, peatlands, seagrass beds, salt marshes and marine and coastal ecosystems that contribute to carbon sequestration”, the report says.
Restoration is “handiest” when it is inclusive of the information and rights of Indigenous peoples and when it covers huge areas, consistent with the report.
A number of the response decisions offered throughout the report assist the implementation or achievement of the Kunming-Montreal World Biodiversity Framework, the UN Sustainable Progress Goals and the Paris Settlement.
The report says:
“The aptitude to contribute to quite a lot of targets concurrently is a regular and extremely efficient attribute of nexus approaches. These response decisions are attributable to this reality a promising mechanism for integrating efforts and accelerating progress in route of quite a lot of protection targets and frameworks.”
Nonetheless, it says, in order to acquire these targets inside a nexus framework, “new types of indicators, information and processes may need to be put into place”. It supplies that current, siloed methods of governance “have resulted in misaligned, duplicative and inconsistent governance and have didn’t cope with direct and indirect drivers of change”.
5. Reforming worldwide financial strategies can also assist shut the biodiversity funding gap
The report identifies the outlet in finance wished to satisfy the desires for biodiversity movement as between $300bn and $1tn per yr.
Furthermore, it says, reaching the UN Sustainable Progress Goals related to the nexus would require on the very least one different $4tn in funding yearly in water, meals, effectively being and native climate change.
Given these huge sums, the report requires “urgent movement” to “deal with the dominance of a slim set of pursuits inside monetary and financial strategies” and improve funding in biodiversity, meals and water. It supplies that these wider reforms would possibly “amplif[y]” the additional funding made throughout the nexus.
For example, regulatory reform would possibly make funding in nature further attractive by rising the costs of biodiversity-harming actions. That’s intently linked to concentrate on 18 of the Kunming-Montreal World Biodiversity Framework, which calls on worldwide places to “take away, half out or reform incentives” which is perhaps harmful to biodiversity.

Aim 18 of the Kunming-Montreal World Biodiversity Framework. Provide: CBD (2022)
In accordance with the report, there’s established nonetheless incomplete proof that the world’s current monetary and financial strategies are contributing to biodiversity loss and resulting in elevated “nature-related risks”, which, it supplies, are “mutually reinforcing with risks from native climate change”.
These risks are estimated to be “throughout the trillions of {{dollars}}”.
Spending “aimed towards enhancing the standing of biodiversity” is estimated at spherical $200bn per yr.
Presently, the world spends 35 events further property on actions that straight harm biodiversity than it does on preserving nature. That’s exacerbated by an additional $300bn spent on illegal actions that damage nature, just like illegal deforestation and wildlife trafficking.
The report identifies three pathways which may help larger align worldwide financial flows for biodiversity and the rest of the nexus:
- Enhancing the provision and use of information on the “varied values of nature”, just like by updating transparency and reporting requirements to duplicate the nexus components.
- Enhancing entry to finance by the use of quite a lot of utterly completely different financial units, along with inexperienced bonds, reformed tax insurance coverage insurance policies and funds for ecosystem suppliers.
- Reducing detrimental incentives, along with by improved funding safeguards and addressing harmful subsidies.
The graphic beneath reveals the current state of funding for the nexus, with biodiversity-harming financial flows confirmed in crimson and biodiversity-positive finance in blue. The icons denote the funding that is directed to each part of the nexus: biodiversity, water, meals, effectively being and native climate change.
The graphic moreover reveals how financial reforms might acquire benefit the nexus by reducing detrimental finance and rising biodiversity-supporting finance.
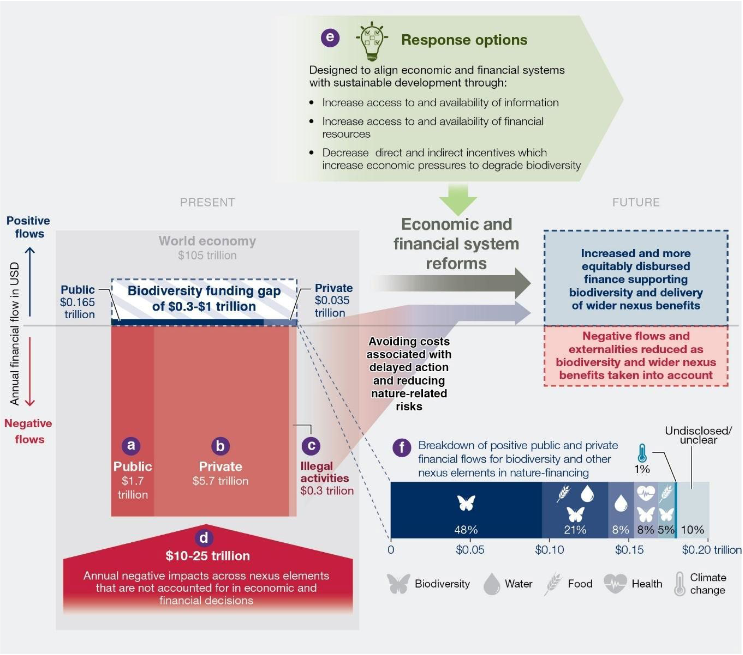
Of the finance that is presently directed in route of biodiversity and the alternative components of the nexus, there are “some current synergies”, the report suggests. Nonetheless, better than half of the funding acknowledged throughout the report goes solely to addressing a single part of the nexus: 48% for biodiversity, 8% for water and 1% for native climate change.
Furthermore, there is a “clear bias” throughout the distribution of biodiversity finance, with public funds primarily concentrated in North America, Europe and China, the report says. On the an identical time, solely 5% of world personal biodiversity finance is allotted to least-developed worldwide places.
Addressing related issues, such as a result of the unsustainable debt burden confronted by rising worldwide places and striving for merely and equitable transitions, can also assist assist financing the nexus as successfully. The report concludes:
“Collectively, these efforts would possibly reform the connection between the monetary system and nature, enhance equity and ship sustainable development outcomes.”
Sharelines from this story
-
IPBES nexus report: 5 takeaways for biodiversity, meals, water, effectively being and native climate
