The amount of UK electrical power generated from fossil fuels fell 22% year-on-year in 2023 to the underside stage since 1957, Carbon Momentary analysis reveals.
The 104 terawatt hours (TWh) generated from fossil fuels in 2023 is the underside stage in 66 years. Once more then, Harold Macmillan was the UK prime minister and the Beatles’ John Lennon and Paul McCartney had merely met for the first time.
Electrical power from fossil fuels has now fallen by two-thirds (199TWh) since peaking in 2008. Inside that entire, coal has dropped by 115TWh (97%) and gasoline by 80TWh (45%).
These declines have been introduced on by the speedy progress of renewable vitality (up six-fold since 2008, some 113TWh) and by lower electrical power demand (down 21% since 2008, some 83TWh).
Consequently, fossil fuels made up merely 33% of UK electrical power offers in 2023 – their lowest ever share – of which gasoline was 31%, coal merely over 1% and oil barely under 1%.
Low-carbon sources made up 56% of the entire, of which renewables had been 43% and nuclear 13%. The remaining is from imports (7%) and totally different sources (3%), harking back to waste incineration.
Basic, {the electrical} power generated inside the UK in 2023 had the lowest-ever carbon depth, with a median of 162g of carbon dioxide per kilowatt hour (gCO2/kWh).
This stays a long way from the federal authorities’s ambition for 95% low-carbon electrical power by 2030 – merely seven years from now – and a completely decarbonised grid by 2035.
Fossil falls
Historically, fossil-fuel period rose steadily as the size of the UK’s financial system expanded – and, relatedly, as demand for electrical power grew.
The rise in demand for electrical power paused in the middle of the late Nineteen Seventies and Nineteen Eighties, as a result of the nation’s monetary state of affairs and industrial relations worsened. However the upwards march rapidly resumed.
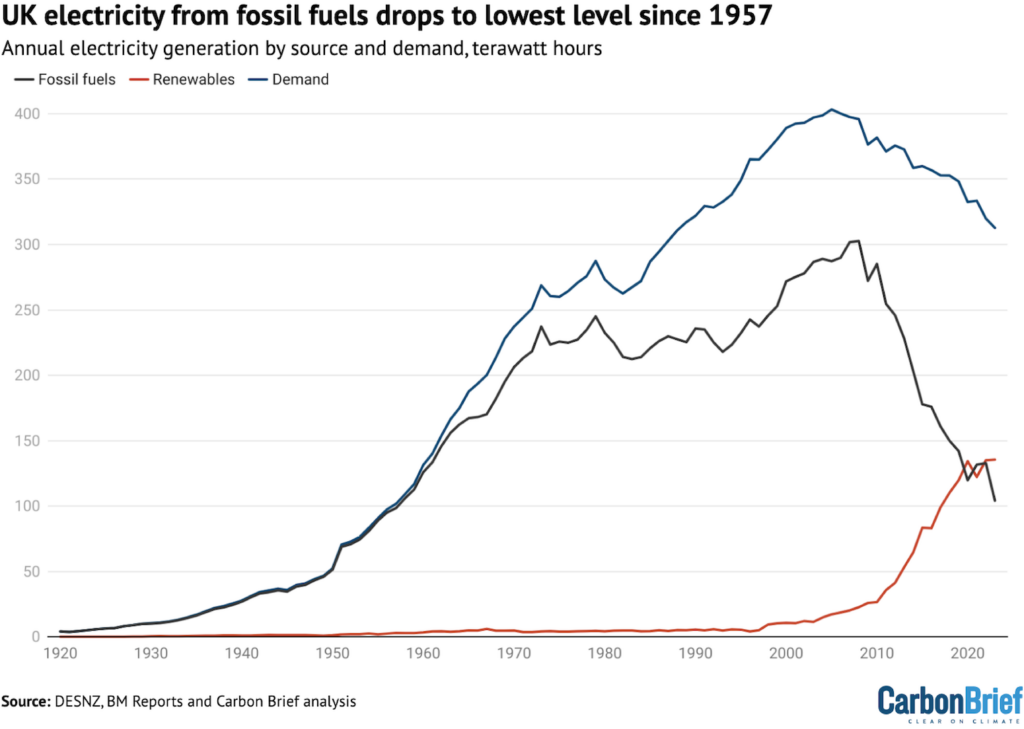
Electrical power demand then started to “decouple” from monetary improvement inside the early 2000s, leading to a peak in 2005. Since then, demand has dropped precipitously, falling from 396TWh in 2008 to 313TWh in 2023, as confirmed by the darkish blue line inside the decide beneath.
This low cost in demand of 83TWh (21%) is the same as larger than 3 occasions the anticipated output of the Hinkley Degree C nuclear power plant, which is presently being constructed in Somerset.
Demand reductions are the outcomes of a poorly understood combination of further atmosphere pleasant residence tools and lighting, extreme prices pushed by expensive gasoline and changes inside the building of the UK as a result of it shifts to an ever further service-led fairly than manufacturing-heavy financial system.
(Inside the medium- to long-term, electrical power demand is anticipated to rise as transport and heating are increasingly more electrified using electrical autos and heat pumps.)
Whereas electrical power demand was falling, the UK was moreover starting to rapidly scale its renewable vitality functionality, primarily from wind, however as well as from photograph voltaic and bioenergy.
Consequently, renewable electrical power output climbed six-fold from 23TWh in 2008 to 135TWh in 2023, confirmed by the purple line inside the chart beneath.
The combined have an effect on of falling demand (-83TWh) and rising renewables (+113TWh) has acted as a pincer on electrical power period from fossil fuels, squeezing it from two directions.
Having peaked at 303TWh in 2008, the UK acquired merely 104TWh {of electrical} power from fossil fuels in 2023 – as confirmed by the steep black line inside the decide beneath – a two-thirds low cost in 15 years. This takes fossil-fuel period to its lowest stage since 1957.
In 1957, the Conservative event’s Harold Macmillan was elected UK prime minister in January following Anthony Eden’s resignation ensuing from unwell effectively being.
That exact same yr, the Central Electrical power Producing Board was established ‘to keep up the lights on’. It was liable for electrical power period, transmission and bulk product sales in England and Wales up until {the electrical} power sector was privatised inside the Nineties.
The world’s first enterprise nuclear power station, at Calder Hall in Cumbria, had merely opened its second unit, however fossil fuels nonetheless supplied 97% of the UK’s electrical power.
Moreover that yr, the Suez canal was reopened, “Sputnik 1” – the first artificial satellite tv for pc television for laptop to orbit Earth – was launched by the Soviet Union and the UK authorities unveiled plans to allow women to affix the Dwelling of Lords for the first time.
Shifting shares
For lots of the earlier century, fossil fuels generated nearly the whole UK’s electrical power, as confirmed by the black line inside the decide beneath. Fossil fuels – predominantly coal – made up 97% of the entire in 1957, a decide that had barely modified for a few years.
The rise of nuclear power (darkish blue line) from the late Fifties onwards – after Calder Hall opened in 1956 – pushed the fossil gasoline share downwards.
However electrical power demand continued to develop and the earliest nuclear reactors had been starting to close down by the early 2000s, with solely Sizewell B in Suffolk, in 1995, having modified them.
With renewables nonetheless of their infancy, this meant that, in 2008, the UK was nonetheless getting 76% of its electrical power from fossil fuels. Of this, 45% was from gasoline and 30% from coal.
Since then, fossil fuels’ share has dropped to a record-low 33% in 2023, being overtaken by renewables inside the course of (purple line).
Renewables’ share reached a file extreme of 43% in 2023, with nuclear (13%, delicate blue line), imports (7%) and totally different sources (3%) making up the remaining.
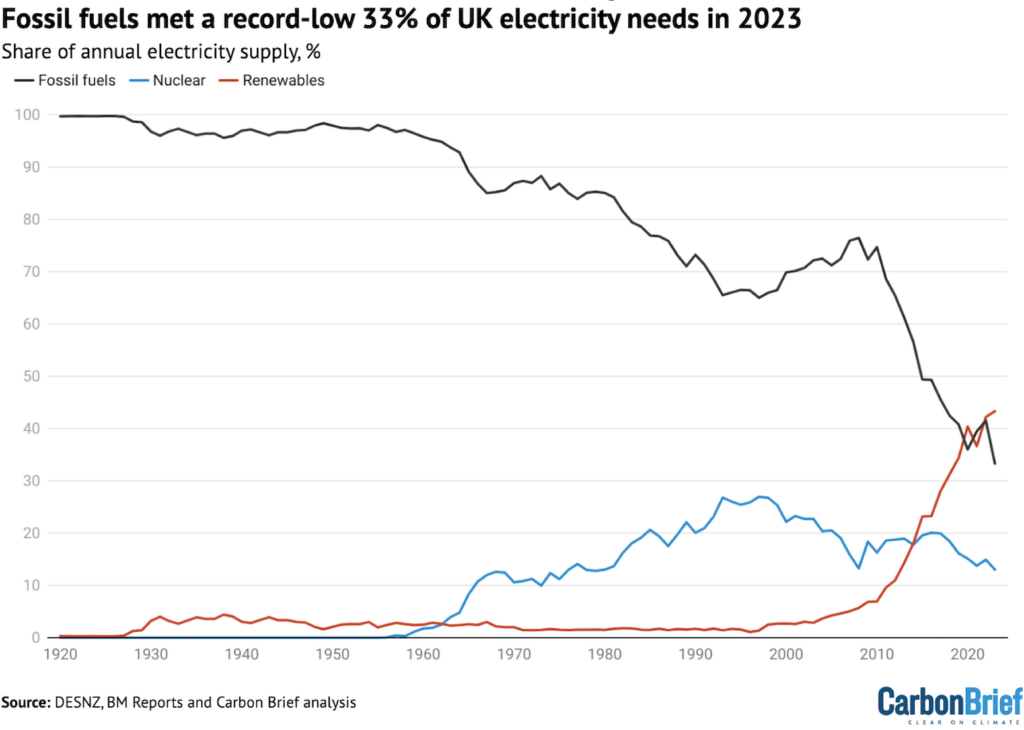
Your entire share from low-carbon sources – renewables and nuclear – was 56% in 2023. This was down one degree from the file 57% share in 2022, due to a drop in nuclear output.
The current authorities’s ambition is to get 95% of the nation’s electrical power from low-carbon sources by 2030, which could indicate an increase of 39 proportion components in seven years.
Up to now, the quickest worth of improve has been 25 proportion components in seven years, achieved between 2010 (23% low-carbon) and 2017 (48%).
The aim is then to completely decarbonise the grid by 2035. The opposition Labour Get collectively’s aim is way more formidable, hoping to completely decarbonise {the electrical} power grid already by 2030. This could be a 44 proportion degree improve in seven years.
Renewable rise
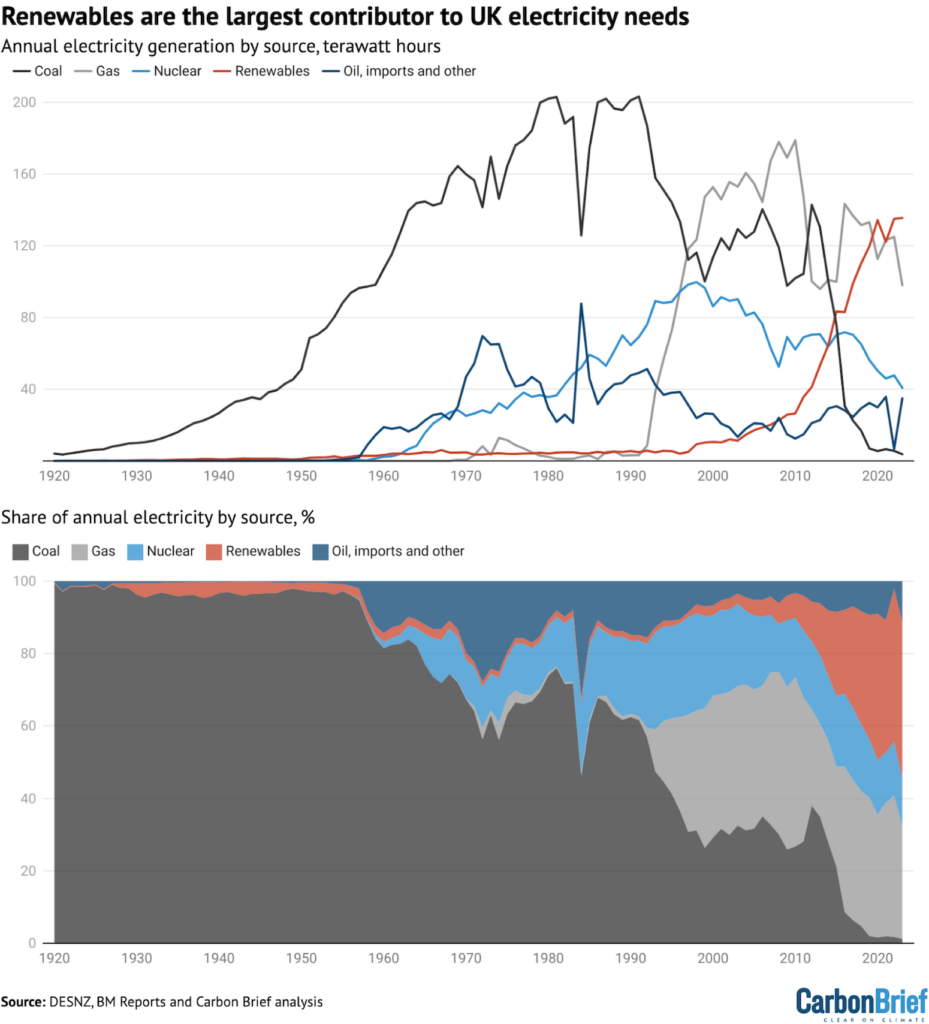
The rise of renewables since 2008 has been virtually as steep because the autumn for fossil fuels, as confirmed by the purple line inside the decide beneath.
Notably, however, since reaching 134TWh in 2020, renewables have efficiently stood nonetheless, with output of 135TWh in 2023, matching the file 135TWh set in 2022.
This shows the stableness between continued will improve in wind and photograph voltaic functionality, variations in frequent local weather conditions and decreased output before now two years from bioenergy.
The 135TWh of renewable electrical power in 2023 was made up of:
- 82TWh from wind (up 2TWh year-on-year, a 2% improve);
- 35TWh from bioenergy (down 5TWh and 13% from 2021 ranges);
- 14TWh from photograph voltaic (up 2% year-on-year);
- 5TWh from hydro (down 1TWh year-on-year, a 9% drop).
On the similar time, coal has virtually disappeared from the UK electrical power system, falling from 119TWh in 2008 to 4TWh in 2023 (down 115TWh, 97%), confirmed by the black line beneath.
Gasoline, within the meantime, is now proper right down to ranges not usually seen given that mid-Nineties (grey line), falling from 178TWh in 2008 to solely 98TWh in 2023 (down 80TWh, 45%).
Nuclear moreover continues to say no, reaching 41TWh in 2023, a 7TWh low cost year-on-year (15%) from already low ranges, after Hinkley Degree B in Somerset closed down and the remaining 5 stations had been rapidly offline for deliberate maintenance outages.
Functionality for every onshore and offshore wind initiatives rose in 2023, by 0.6GW and 1.1GW, respectively.
Widespread wind speeds inside the first 11 months of 2023 had been correctly beneath the long-term frequent however, in accordance with authorities figures, whereas 2022 had solely been marginally beneath frequent. This muted common period improvement over the previous yr significantly.
A windy December helped improve common period figures for the yr, with a model new wind period file provisionally set on 21 December in accordance with Nationwide Grid ESO. Wind period hit 21.8GW between 8:00 and eight:30 on 21 December, providing 56% of the period mix.
Notably, only one offshore windfarm was completed in 2023 – the 1GW Seagreen progress off the east coast of Scotland – whereas three initiatives totalling 3GW had been commissioned in 2022.
In October 2023, Dogger Monetary establishment off the coast of Yorkshire despatched power to the nationwide grid for the first time. Will in all probability be the world’s largest offshore windfarm, at 3.6GW, when it is completed in 2026.
Nevertheless, the federal authorities’s ambition for 50GW of offshore wind by 2030 is uncertain after the latest public sale for model new renewable functionality did not protected any further initiatives.
For bioenergy, the 35TWh in 2023 was identical to the extent delivered in 2022, nonetheless down from 40TWh in 2020 and 2021. Plant biomass – primarily woodchips – is spherical two-thirds of these annual totals.
The 4 wood-burning former coal objects on the Drax plant in Yorkshire account for spherical one-third of power from bioenergy on their very personal. Nonetheless, their output has been subdued in 2022 and 2023, with some reporting having raised questions regarding the incentives at play.
Within the meantime, electrical power period from photo voltaic power solely elevated by 2% in 2023, no matter a surge in new functionality being linked to the grid.
The number of hours of sunshine all through 2023 was roughly in line with the long-term frequent, authorities figures current, whereas 2022 had been unusually sunny.
Primarily based on figures from consultancy Rystad Energy cited by Drax Electrical Insights, the UK’s photograph voltaic functionality was anticipated to rise from 15GW firstly of 2023 to 18GW by the highest of the yr.
Present improvement in photograph voltaic installations comes after an extended interval of stagnation, with put in functionality having reached 13GW in 2018 and solely climbing to 14GW in 2022.
Rystad Energy expects UK photograph voltaic functionality to proceed accelerating, topping 25GW in 2025.
The newest low cost in coal period, down one different 33% in 2023, bought right here as three of the UK’s 4 remaining coal-fired power stations shut down.
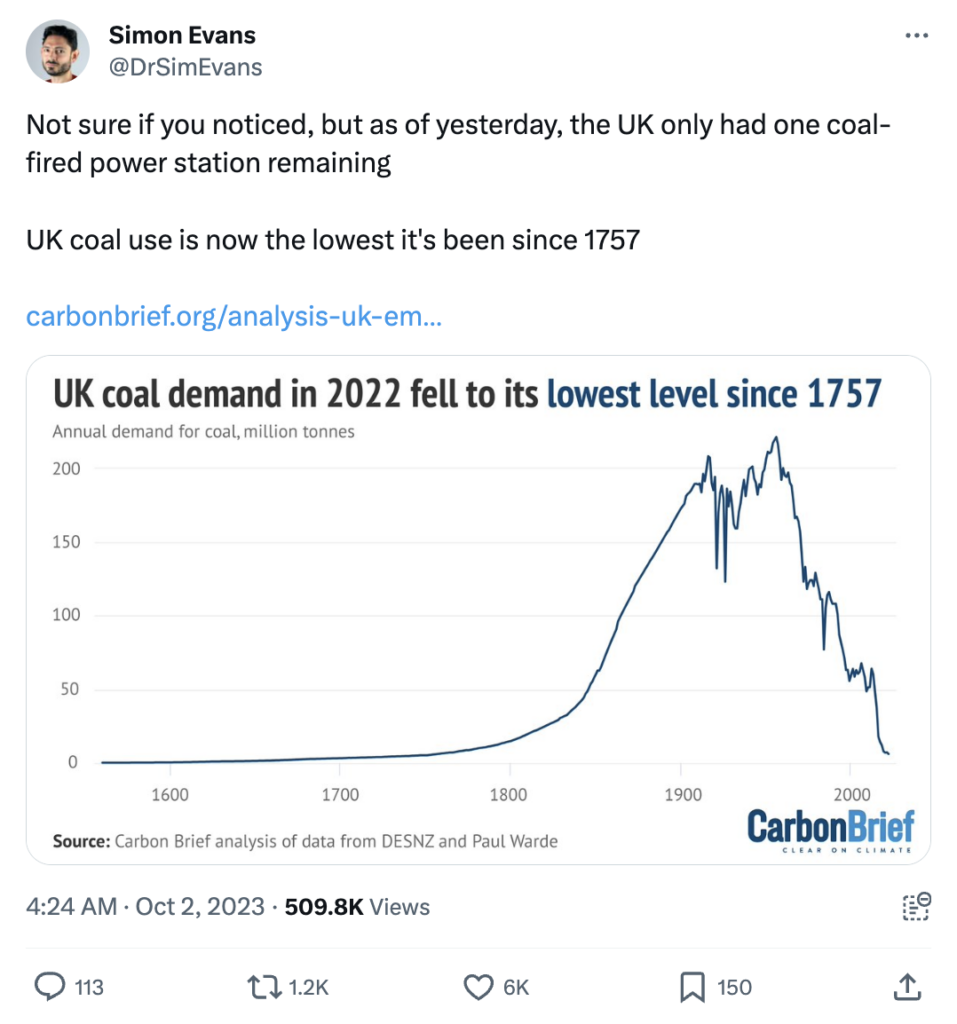
West Burton in Nottinghamshire closed in March, then Drax in Yorkshire closed in April, adopted by Kilroot in Northern Ireland on the end of September.
Solely Ratcliffe in Nottinghamshire, operated by utility company Uniper, stays operational. It plans to close in September 2024, ahead of the federal authorities’s ambition to complete coal power by October 2024.
Whereas the UK seen a severe coal-to-gas transition inside the Nineties “dash for gasoline”, present reductions in coal use have been pushed by renewables and decreased demand. These similar forces have moreover been driving gasoline out of the combo.
The huge drop in gasoline period in 2023 of 27TWh (21%) shows a mixture of this longer-term improvement with a one-off flip inside the UK’s electrical power imports.
The dip in the dead of night blue line for “oil, imports and totally different” in 2022 is because of UK becoming a web electrical power exporter that yr for the first time ever.
Yearly given that opening of the first “interconnector” linking the grids of the UK and France in 1986, the UK has been a web electrical power importer – apart from 2022.
The swap in 2022 was ensuing from widespread outages inside the French nuclear fleet, with neighbouring worldwide places along with the UK selecting up the slack.
In 2023, the UK reverted to being a web importer, looking for 23TWh {of electrical} power from worldwide places along with France, the Netherlands, Belgium and Norway. This was identical to 2021 (25TWh).
The swap from being a web exporter of 5TWh in 2022 to web imports of 23TWh in 2023 combined with common output from renewables and falling demand to push down the need for fossil fuels.
The UK now has 8.4 gigawatts (GW) of interconnector functionality to hyperlink its electrical power system with that of neighbouring worldwide places. Some 4.4GW of this has been added before now 5 years.
In addition to, the 1.4GW Viking Hyperlink interconnector between the UK and Denmark was completed in late 2023, and started engaged on 29 December.
One different 4.7GW has regulatory approval, with further initiatives totalling 5.6GW moreover deliberate.
Cleanest power
With fossil fuels reaching a record-low 33% share and coal proper right down to 1% of the entire, the UK seen its lowest-carbon electrical power mix ever in 2023.
The carbon depth {of electrical} power – in numerous phrases, the amount of CO2 associated to each unit {of electrical} power – fell to a record-low 162gCO2/kWh in 2023, a reduction of 18% year-on-year.
This continues a longer-term improvement, confirmed inside the decide beneath. Inside the early years of the gathering, the reductions in carbon depth replicate a shift within the course of additional atmosphere pleasant power crops.
The expansion of nuclear power inside the Nineteen Seventies and Nineteen Eighties was adopted by the “dash for gasoline”, which is lower-carbon than coal. From spherical 2008, the decline is because of rise of renewables.
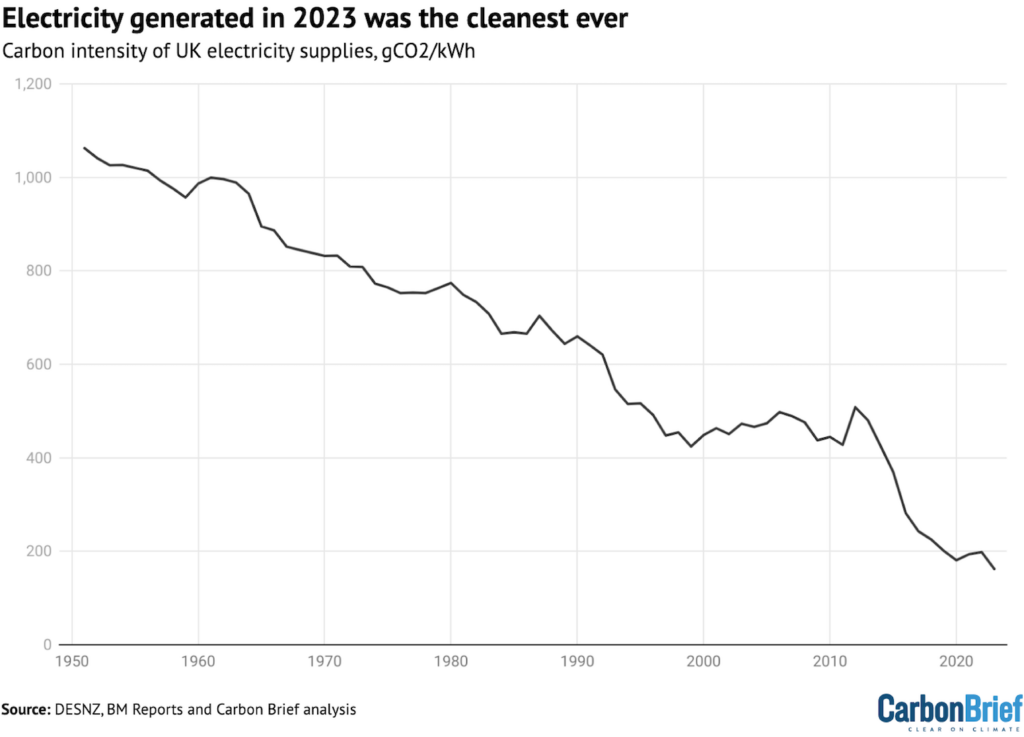
The federal authorities had earlier set a goal of reducing the carbon depth {of electrical} power period to beneath 100gCO2/kWh by 2030. Since then, the UK’s 2050 native climate aim has been strengthened from an 80% decrease in emissions to a 100% decrease – reaching net-zero by that date.
If the federal authorities reaches its aim of 95% low-carbon electrical power by 2030 then the carbon depth of period would fall to well-below 100gCO2/kWh. Merely how far beneath would depend on the contribution from bioenergy and whether or not or not CO2 associated to imported electrical power is counted.
The decide above counts bioenergy lifecycle emissions and imports within the course of the entire.
Methodology
The figures inside the article are from Carbon Momentary analysis of data from DESNZ Energy Traits chapter 5 and chapter 6, along with from BM Experiences. The figures from BM Experiences are for electrical power supplied to the grid in Good Britain solely and are adjusted to include Northern Ireland.
In Carbon Momentary’s analysis, the BM Experiences numbers are moreover adjusted to account for electrical power utilized by power crops on web page and for period by crops not linked to the high-voltage nationwide grid. This consists of many onshore windfarms, along with industrial gasoline combined heat and power crops and other people burning landfill gasoline, waste or sewage gasoline.
The analysis of carbon depth relies on the methodology printed by Nationwide Grid ESO, however as well as takes account of gasoline use effectivity for earlier years.
DESNZ historic electrical power info, along with years sooner than 2009, is adjusted in line with totally different figures and combined with info on imports from a separate DESNZ dataset. Observe that the knowledge earlier to 1951 solely consists of “fundamental” power producers.
This textual content was written by Simon Evans. Data analysis was carried out by Simon Evans and Verner Viisainen.
Sharelines from this story
