Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from fossil fuels and cement will rise round 0.8% in 2024, reaching a document 37.4bn tonnes of CO2 (GtCO2), in keeping with the 2024 International Carbon Price range report by the International Carbon Venture.
That is 0.4GtCO2 larger than the earlier document, set in 2023.
Complete CO2 emissions – together with each fossil and land-use emissions – may even set a brand new document at 41.6GtCO2, reflecting a progress of two% over 2023 ranges.
That is due, partially, to larger than traditional land-use emissions pushed by excessive wildfire exercise in South America.
Regardless of the rise in 2024, whole CO2 emissions have largely plateaued over the previous decade, an indication that the world is making some modest progress tackling emissions.
However a flattening of emissions is way from what is required to convey international emissions right down to zero and stabilise international temperatures in-line with Paris Settlement targets.
The nineteenth version of the International Carbon Price range, which is revealed at this time, additionally reveals:
- Emissions emissions are projected to lower considerably within the EU (down 3.8%) and barely within the US (down 0.6%) in 2024. They’re anticipated to extend barely in China (up 0.2%), and enhance considerably in India (up 4.6%) and the remainder of the world (up 1.6%, together with worldwide delivery and aviation).
- International emissions from coal elevated by 0.2% in 2024 in comparison with 2023, whereas oil emissions elevated 0.9% and fuel emissions elevated by 2.4%. Emissions from cement and different sources fell by 2.8%.
- International land-use emissions clocked in at 4.2GtCO2 in 2024. This represents a 0.5GtCO2 enhance over 2023 and was primarily pushed by wildfire emissions linked to deforestation and forest degradation in South America. Total, land-use emissions have decreased by round 28% since their peak within the late-Nineteen Nineties, with a very massive drop prior to now decade.
- Whereas the land sink was fairly weak in 2023 – main to hypothesis that it might be on a path towards collapse – it seems to have largely recovered again to shut to its common for the previous decade.
- If international emissions stay at present ranges, the remaining carbon finances to restrict warming to 1.5C (with a 50% likelihood) can be exhausted within the subsequent six years. Carbon budgets to restrict warming to 1.7C and 2C would equally be used up in 15 and 27 years, respectively.
- The focus of CO2 within the ambiance is about to achieve 422.5 components per million (ppm) in 2024, 2.8ppm above 2023 and 52% above pre-industrial ranges.
Each international fossil and whole CO2 emissions at document ranges
The 2024 International Carbon Price range finds that CO2 emissions from fossil use are projected to rise 0.8% in 2024, reaching a document 37.4GtCO2 – 0.4GtCO2 larger than the earlier document, set final yr.
Complete CO2 emissions, which embrace land-use change, are additionally anticipated to achieve document highs at 41.6GtCO2, or 2.0% above the earlier document set in 2023.
This huge enhance was pushed each by constant progress in fossil-fuel emissions and abnormally excessive land-use emissions in 2024 – due partially to wildfires in South America exacerbated by a robust El Niño occasion and excessive temperatures.
Annually the International Carbon Price range is up to date to incorporate the newest information in addition to enhancements to modelling sources and sinks, leading to some year-to-year revisions to the historic document.
The determine beneath reveals the 2024 international CO2 emissions replace (darkish blue stable line) alongside 2023 (gray dotted) 2022 (yellow dotted), 2021 (vibrant blue dotted) and 2020 (pink dotted). The shaded space signifies the uncertainty across the new 2024 finances.
The 2024 figures are usually fairly just like these within the 2023 International Carbon Price range, although they present considerably larger emissions previous to 1980 and barely decrease emissions over the previous seven years. Revisions to the info imply that 2023 is not a hair beneath 2019 ranges, as was reported by Carbon Transient final yr, however somewhat exceeds them by practically 0.5GtCO2.
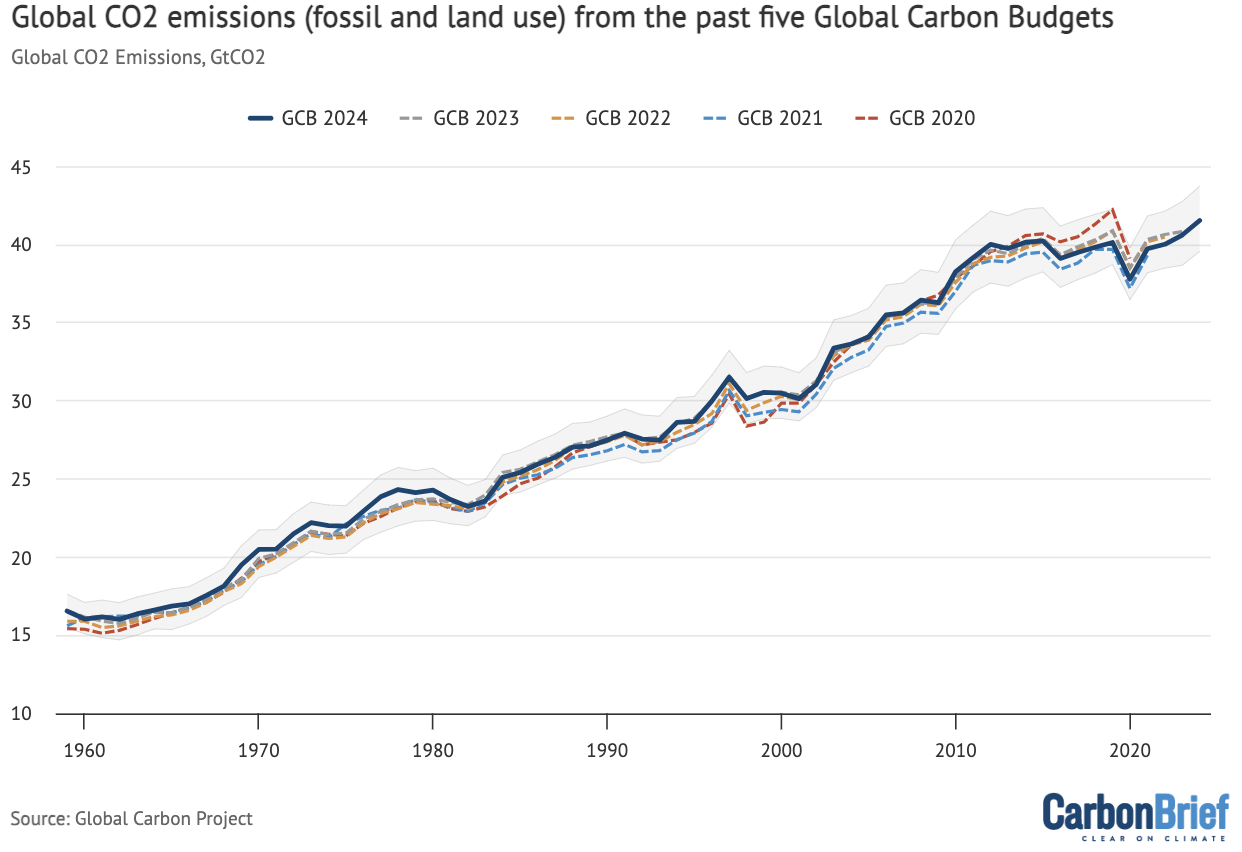
Annual whole international CO2 emissions – from fossil and land-use change – between 1959 and 2024 for the 2020, 2021, 2022, 2023 and 2024 variations of the International Carbon Venture’s International Carbon Price range, in billions of tonnes of CO2 per yr (GtCO2). Shaded space reveals the estimated one-sigma uncertainty for the 2024 finances. Information from the International Carbon Venture; chart by Carbon Transient.
Complete international CO2 emissions have notably plateaued prior to now decade (2015-24), rising at solely 0.2% per yr in comparison with the 1.9% price of progress over the earlier decade (2005-214) and the longer-term common progress price of 1.7% between 1959 and 2014.
This obvious flattening is because of declining land-use emissions compensating for continued will increase in fossil CO2 emissions. Fossil emissions grew round 0.2GtCO2 per yr over the previous decade, whereas land-use emissions decreased by a comparable quantity.
Nonetheless, regardless of the emissions plateau, there’s nonetheless no signal of the speedy and deep lower in CO2 emissions wanted to achieve net-zero and stabilise international temperatures in-line with Paris Settlement targets.
If international emissions stay at present ranges, the remaining carbon finances to restrict warming to 1.5C (with a 50% likelihood) can be exhausted within the subsequent six years. Carbon budgets to restrict warming to 1.7C and 2C would equally be used up in 15 and 27 years, respectively.
International fossil CO2 emissions additionally grew extra slowly prior to now decade (0.7% per yr) in comparison with the earlier decade (2.1%). This was pushed by the continued decarbonisation of vitality techniques – together with a shift from burning coal to fuel and changing fossil fuels with renewables – in addition to barely weaker international financial progress in the course of the previous decade.
The determine beneath breaks down international emissions (darkish blue line) within the 2024 finances into fossil (mid blue) and land-use (gentle blue) elements. Fossil CO2 emissions signify the majority of whole international emissions in recent times, accounting for roughly 90% of emissions in 2024 (in comparison with 10% for land use). This represents a big change from the primary half of the twentieth century, when land-use emissions had been roughly the identical as fossil emissions.
International fossil emissions embrace CO2 emitted from burning coal, oil and fuel, in addition to the manufacturing of cement. Nonetheless, the International Carbon Price range additionally subtracts the cement carbonation sink – CO2 slowly absorbed by cement as soon as it’s uncovered to the air – from fossil emissions in annually to find out whole fossil emissions.
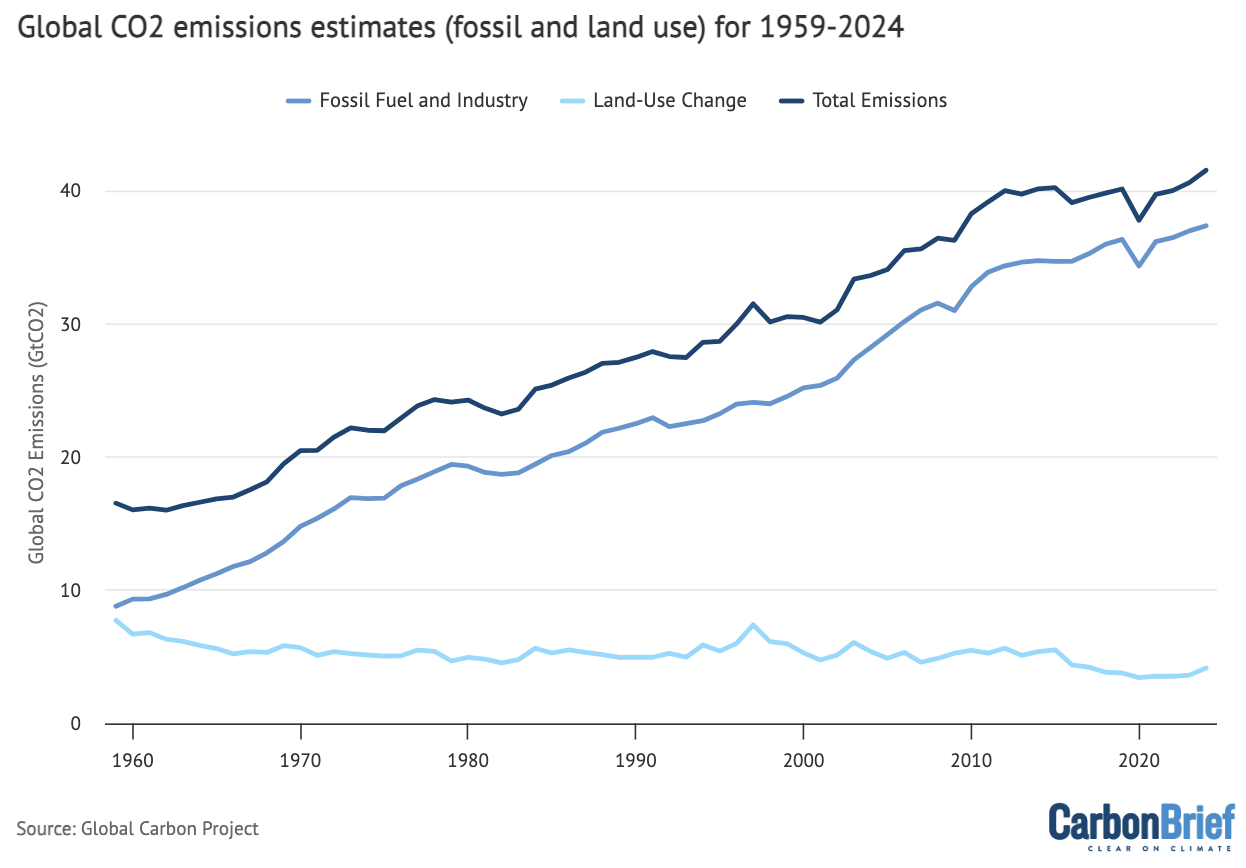
International CO2 emissions separated out into fossil and land-use change elements between 1959 and 2024 from the 2024 International Carbon Price range. Notice that fossil CO2 emissions are inclusive of the cement carbonation sink. Information from the International Carbon Venture; chart by Carbon Transient.
International emissions can be expressed on a per-capita foundation, as proven within the determine beneath. Whereas it’s finally whole international emissions that matter for the Earth’s local weather – and a world per-capita determine glosses over lots of variation amongst and inside nations it’s noteworthy that international per-capita emissions peaked in 2012 and have been barely declining within the years since.
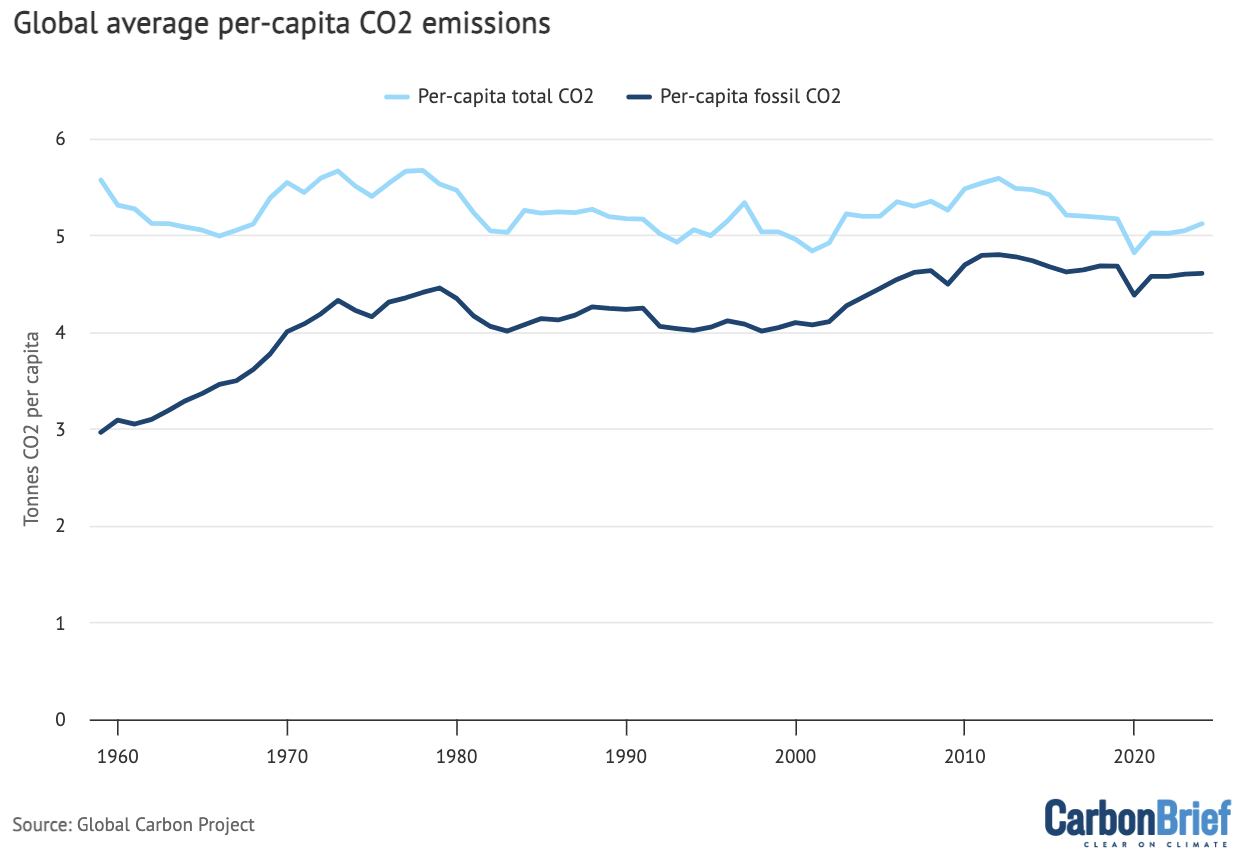
International per-capita CO2 emissions between 1959 and 2024. Notice that fossil CO2 emissions are inclusive of the cement carbonation sink. Information from the International Carbon Venture; chart by Carbon Transient.
Land-use emissions trending downward
International land-use emissions stem from deforestation, degradation, lack of peatlands and harvesting bushes for wooden. They averaged 4GtCO2 over the previous decade (2015-24) and the International Carbon Price range gives an preliminary projection for 2024 of 4.2GtCO2.
This represents a 0.5GtCO2 enhance over land-use emissions in 2023. This was primarily pushed by wildfire emissions linked to deforestation and forest degradation in South America. Drought circumstances related to this yr’s El Niño occasion contributed to the severity of the fires.
Total, land-use emissions have decreased by round 28% since their peak within the late-Nineteen Nineties, with a very massive drop prior to now decade.
This decline is statistically important and is due each to lowering deforestation and growing ranges of reforestation and afforestation globally (although charges of reforestation and afforestation have largely stagnated over the previous decade).
This yr’s International Carbon Price range options various vital enhancements to land-use change emissions estimates, together with up to date estimates of cropland and pasture space in main nations.
4 nations – Brazil, Indonesia, China and the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) – collectively contribute roughly 60% of the worldwide land-use emissions.
The determine beneath reveals adjustments in emissions over time in these nations, in addition to land-use emissions in the remainder of the world (gray). Notice that Chinese language land-use emissions are damaging in recent times.
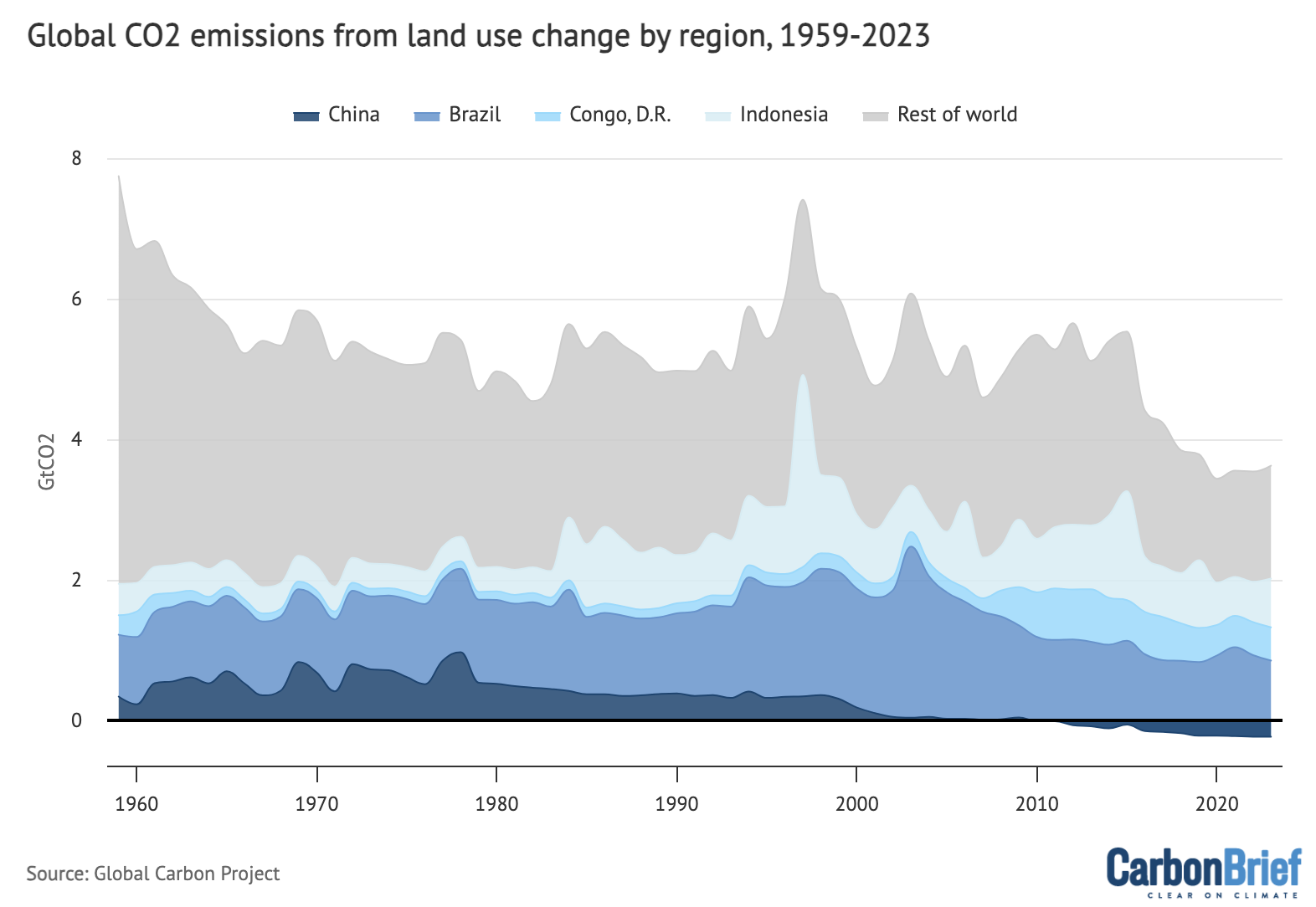
Annual CO2 emissions from land-use change by main emitting nations and the remainder of world over 1959-2023. Notice that country-level land-use change emissions are usually not but accessible for 2024. Information from the International Carbon Venture; chart by Carbon Transient.
Fossil CO2 in main emitting nations
International emissions of fossil CO2 – together with coal, oil, fuel and cement – elevated by round 0.8% in 2024, relative to 2023, with an uncertainty vary of -0.3% to 1.9%. This represents a brand new document excessive and is 2.6% above the 2019 pre-Covid ranges.
The determine beneath reveals international CO2 emissions from fossil fuels, divided into emissions from main emitting nations together with China (darkish blue shading), India (mid blue), the US (gentle blue), EU (pale blue) and the rest of the world (gray).
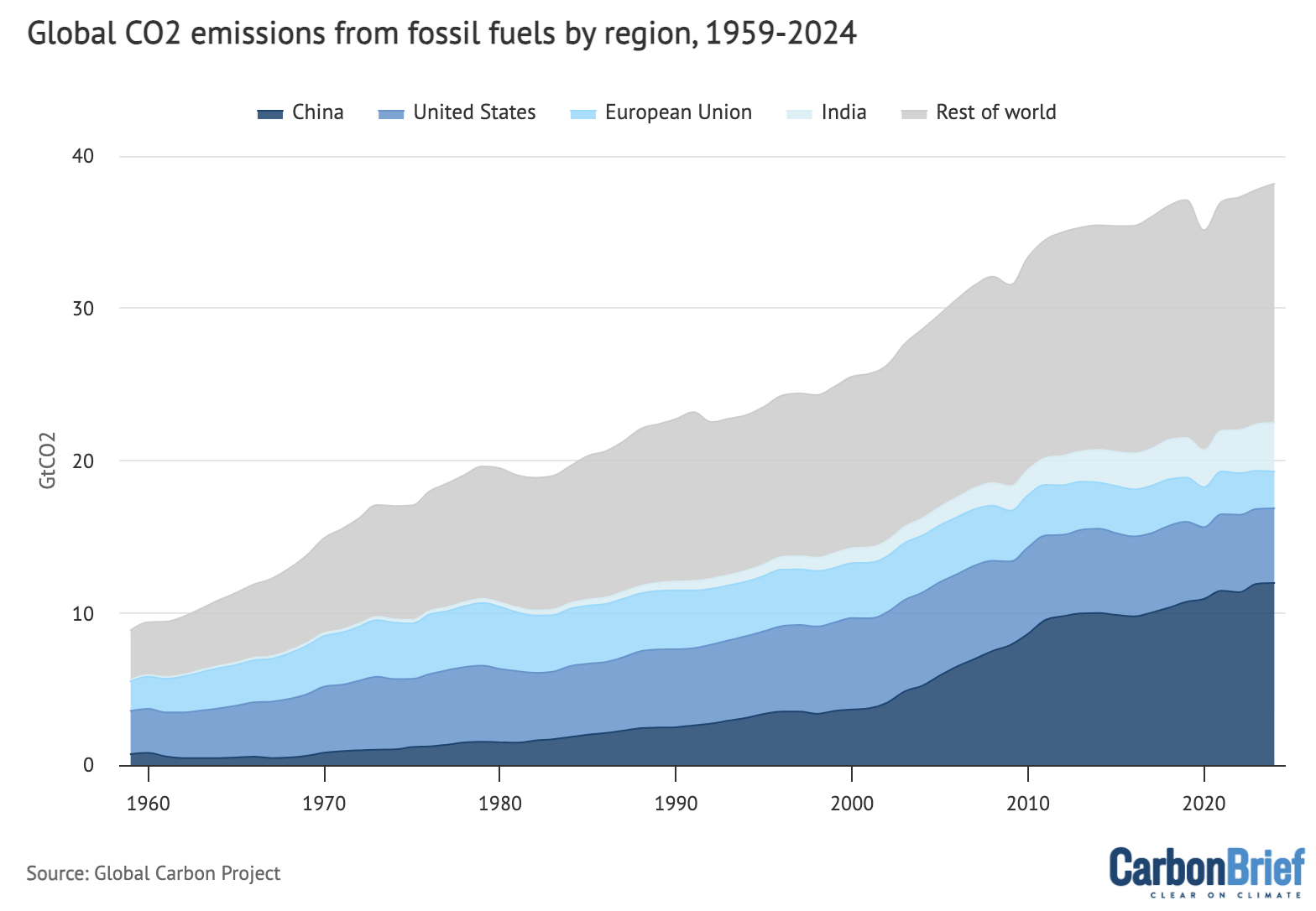
Annual fossil CO2 emissions by main nations and the remainder of the world over 1959-2024, excluding the cement carbonation sink as national-level values are usually not accessible. Information from the International Carbon Venture; chart by Carbon Transient.
For this yr, China represents 32% of worldwide CO2 emissions. Their emissions in 2024 are projected to extend by a comparatively small 0.2% (with an uncertainty vary of -1.6% to +2%), pushed by a small rise in emissions from coal (0.3%) and a big rise in pure fuel emissions (8%). Emissions from oil are anticipated to lower modestly (-0.8%), whereas emissions from cement are anticipated to fall sharply (-8.1%).
The International Carbon Price range report means that Chinese language oil emissions have most likely already peaked, reflecting the acceleration of auto electrification.
India represents 8% of worldwide emissions. In 2024, Indian emissions are projected to extend by 4.6% (with a spread from 3.0% to six.1%), with a 4.5% enhance in emissions from coal, a 3.6% enhance in emissions from oil, a 11.8% enhance in emissions from pure fuel and a 4% enhance in emissions from cement.
Whereas renewable vitality is increasing shortly in India, it stays far slower than the speed of energy demand progress because the financial system quickly expands.
The US represents 13% of worldwide emissions this yr – although is liable for a a lot bigger portion of historic emissions and related atmospheric accumulation of CO2.
US emissions are projected to lower by 0.6% in 2024 (starting from -2.9% to +1.7%). That is being pushed by a modest lower in coal emissions (falling 3.5%). Oil emissions are anticipated to say no by a slight 0.7%, reflecting the rise of electrical automobiles, whereas emissions from fuel are anticipated to extend by 1%.
The EU represents 7% of worldwide emissions. EU emissions are anticipated to lower by 3.8% in 2024, pushed by a 15.8% decline in coal emissions, a 1.3% decline in pure fuel emissions, and a 3.5% decline in cement emissions. EU oil emissions are anticipated to extend barely, by 0.2%.
The EU’s general emissions decline is being pushed by a mix of speedy clear vitality adoption in addition to comparatively weak financial progress and excessive vitality costs.
Worldwide aviation and delivery (included within the “remainder of world” within the determine above) are liable for 3% of worldwide emissions. They’re projected to extend by
7.8% in 2024, however stay beneath their 2019 pre-pandemic degree by 3.5%.
The remainder of the world (excluding aviation) represents 38% of worldwide emissions. Emissions are anticipated to develop by 1.1% in 2024 (starting from -1.0% to +3.3%), with will increase in emissions from coal (0.5%), oil (0.5%), pure fuel (2.2%) and cement (2%).
Total, emissions are projected to lower within the EU and US in 2024, enhance barely in China, and enhance considerably in India and the remainder of the world.
The entire emissions for annually between 2021 and 2024, in addition to the nations and areas that had been liable for the adjustments in absolute emissions, are proven within the determine beneath.
Annual emissions for 2021, 2022, 2023 and estimates for 2024 are proven by the navy blue bars. The smaller bars present the change in emissions between every set of years, damaged down by nation or area – the US (darkish blue), EU (mid blue), China (gentle blue), India (pale blue) and the remainder of the world (gray). Adverse values present reductions in emissions, whereas constructive values replicate emission will increase.
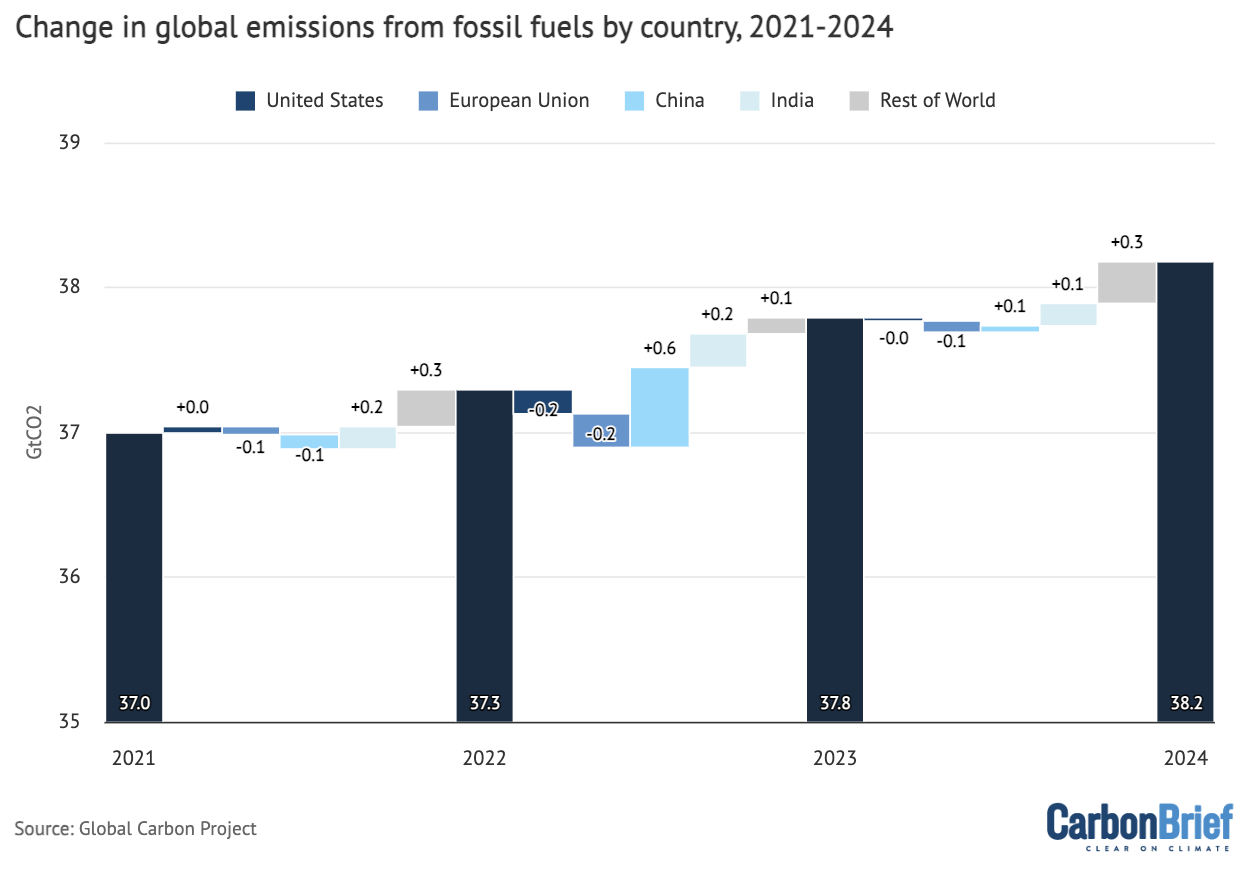
Annual international CO2 emissions from fossil fuels (navy blue bars) and drivers of adjustments between years by nation (smaller bars), excluding the cement carbonation sink as national-level values are usually not accessible. Adverse values point out reductions in emissions. Notice that the y-axis doesn’t begin at zero. Information from the International Carbon Venture; chart by Carbon Transient.
The International Carbon Venture notes that emissions have declined over the previous decade (2014-23) in 22 nations – up from 18 nations in the course of the decade previous to that (2004-13). This lower comes regardless of continued home financial progress and represents a long-term decoupling of CO2 emissions and the financial system.
CO2 emissions decreased in Organisation for Financial Co-operation and Growth (OECD) nations by 1.4% per yr over the previous decade, in comparison with a lower of 0.9% per yr within the decade prior. Non-OECD nations noticed their emissions develop extra slowly (1.8%) over the past decade than the prior one (4.9%).
Development in emissions from coal, oil, and fuel
International fossil-fuel emissions primarily consequence from the combustion of coal, oil and pure fuel. Coal is liable for extra emissions than another fossil gasoline, representing roughly 41% of worldwide fossil CO2 emissions in 2024. Oil is the second largest contributor at 33% of fossil CO2, whereas fuel rounds out the pack at 22%.
These percentages replicate each the quantity of every fossil gasoline consumed globally, but in addition variations in CO2 intensities. Coal leads to probably the most CO2 emitted per unit of warmth or vitality produced, adopted by oil and pure fuel.
The determine beneath reveals international CO2 emissions from totally different fuels over time, masking coal (darkish blue shading), oil (mid blue) and fuel (gentle blue), in addition to cement manufacturing (pale blue) and different sources (gray).
Whereas coal emissions elevated quickly within the mid-2000s, it has largely plateaued since 2013. Nonetheless, coal use elevated considerably in 2021 after which barely within the subsequent three years.
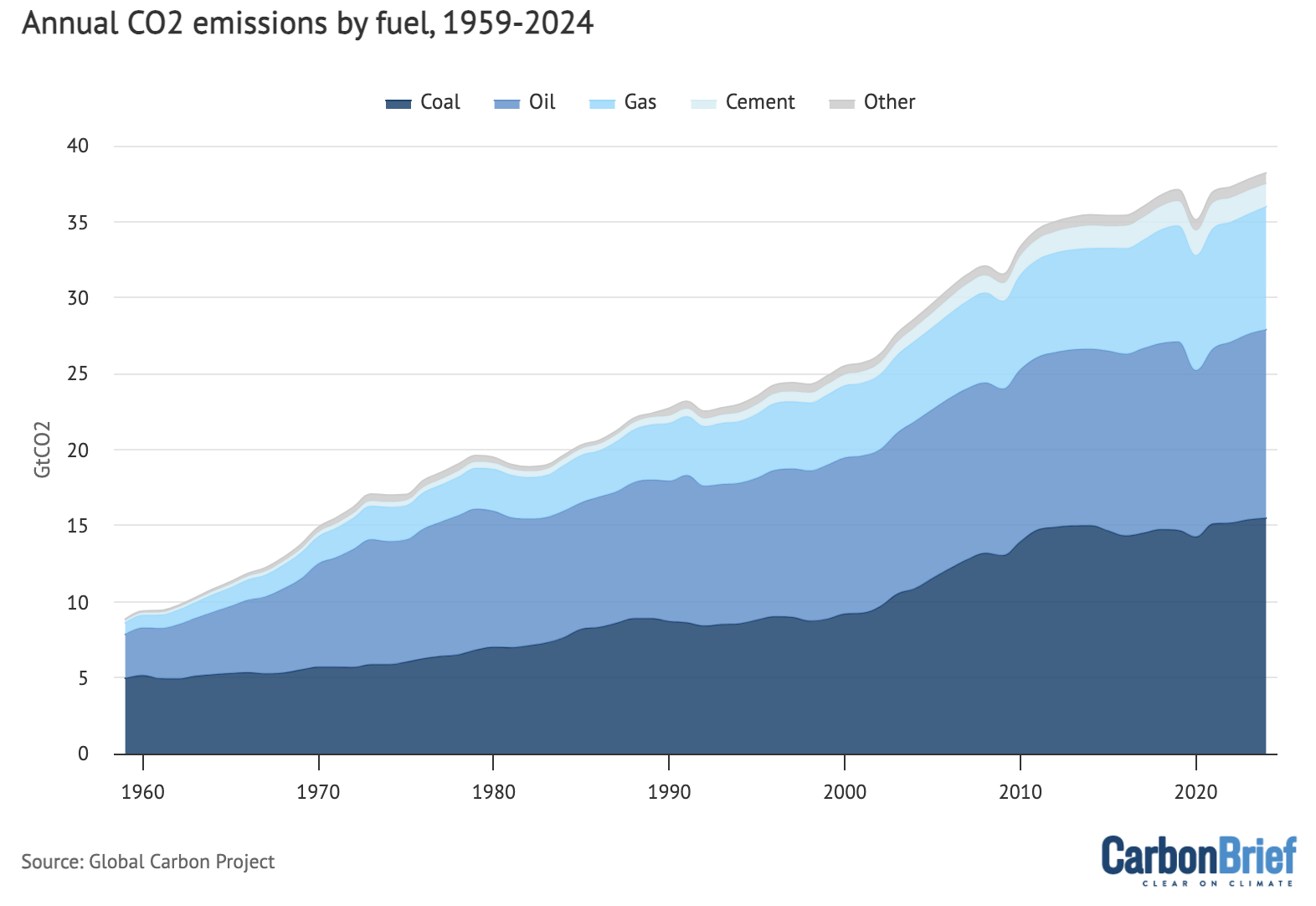
Annual CO2 emissions by fossil gasoline over 1959-2024, excluding the cement carbonation sink. Information from the International Carbon Venture; chart by Carbon Transient.
International emissions from coal elevated by 0.2% in 2024 in comparison with 2023, whereas oil emissions elevated 0.9% and fuel emissions elevated by 2.4%. Emissions from cement and different sources fell by 3%.
Regardless of setting a brand new document this yr, international coal use is just 3% above 2013 ranges – a full 12 years in the past. Against this, in the course of the 2000s, international coal use grew at a price of round 4% each single yr.
The entire emissions for annually between 2021 and 2024 (navy blue bars), in addition to absolutely the change in emissions for every gasoline between years, are proven within the determine beneath.
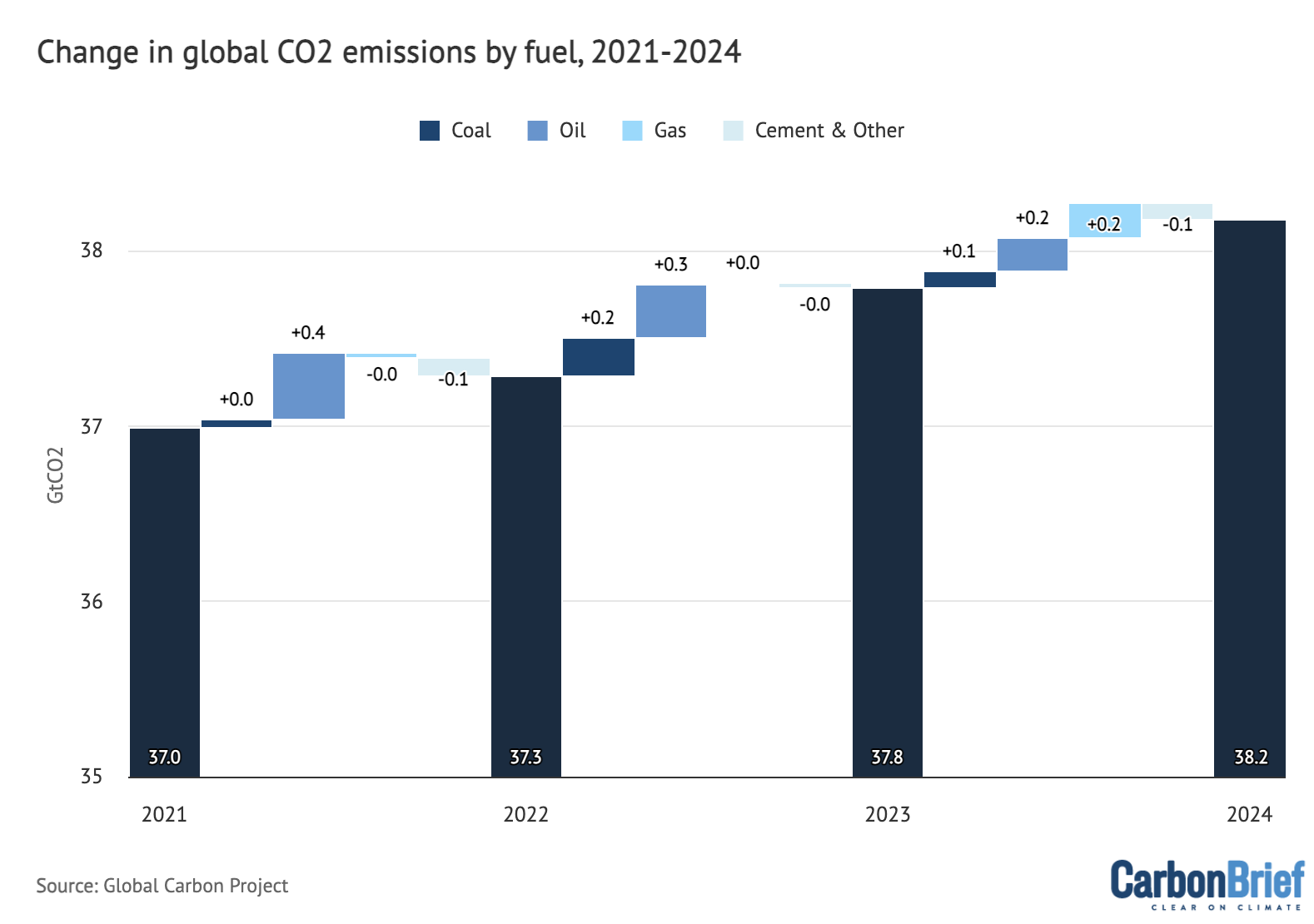
Annual international CO2 emissions from fossil fuels (navy blue bars) and drivers of adjustments between years by gasoline, excluding the cement carbonation sink. Adverse values point out reductions in emissions. Notice that the y-axis doesn’t begin at zero. Information from the International Carbon Venture; chart by Carbon Transient.
Despite the fact that they’ve been growing over the previous 4 years, international CO2 emissions from oil stay very barely (0.8%) beneath the pre-pandemic highs of 2019.
The worldwide carbon finances
Yearly, the International Carbon Venture gives an estimate of the general “international carbon finances”. That is primarily based on estimates of the discharge of CO2 by human exercise and its uptake by the oceans and land, with the rest including to atmospheric concentrations of the fuel.
(This differs from the generally used time period “remaining carbon finances”, which refers back to the quantity of CO2 that may be launched whereas preserving warming beneath international limits of 1.5 or 2C.)
The newest finances, together with estimated values for 2024, is proven within the determine beneath. Values above zero signify sources of CO2 – from fossil fuels and business (darkish blue shading) and land use (mid blue) – whereas values beneath zero signify “carbon sinks” that take away CO2 from the ambiance. Any CO2 emissions that aren’t absorbed by the oceans (gentle gray) or land vegetation (mid gray) accumulate within the ambiance (darkish gray).
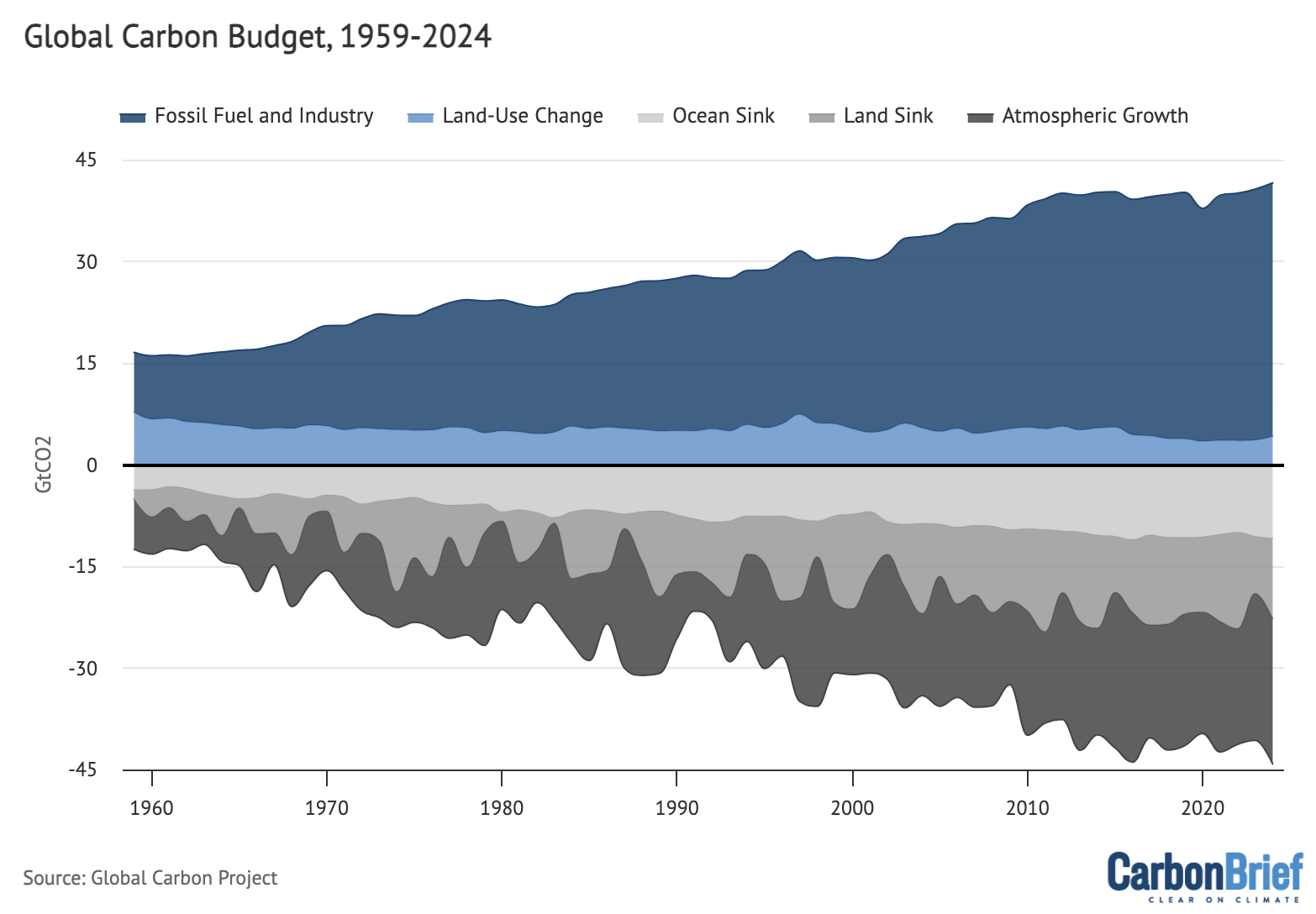
Annual international carbon finances of sources and sinks over 1959-2024. Fossil CO2 emissions embrace the cement carbonation sink. Notice that the finances doesn’t totally stability yearly because of remaining uncertainties, notably in sinks. Information from the International Carbon Venture; chart by Carbon Transient.
Over the previous decade (2015-24), the world’s oceans have taken up roughly 26.5% of whole human emissions, or round 10.6GtCO2 per yr. The ocean CO2 sink has been comparatively flat since 2016 after rising quickly over the prior a long time, reflecting the plateauing of worldwide emissions throughout that interval.
The land sink takes up round 29% of worldwide emissions, or 11.5GtCO2 per yr on common. Whereas the land sink was fairly weak in 2023 – main some to take a position that it might be on a path towards collapse – it seems to have largely recovered again to shut to its common degree over the previous decade in 2024 as El Niño circumstances have pale.
International CO2 emissions from fires had been fairly excessive in 2024, round 7GtCO2 over the primary 10 months of the yr and just like the above common values in 2023.
This was pushed by massive emissions in North and South America, notably in Canada and Brazil. (It isn’t doable to make a direct comparability between reported fireplace CO2 emissions and different elements of the worldwide carbon finances as they already present up in each components of the land sink and land-use emissions.)
Total, the affect of the continuing emissions from human exercise is that atmospheric CO2 continues to extend.
The expansion price of atmospheric CO2 in 2024 is predicted to be round 2.76ppm, which is above common in comparison with the speed of two.46% over the previous decade (2014-23).
The 2024 rise in atmospheric CO2 focus was the fifth largest over the 1959-2024 interval, carefully following 2023, 2015, 2016 and 1998 – most of which had been robust El Niño years.
Atmospheric CO2 concentrations are set to achieve an annual common of 422.5ppm in 2024, representing a rise of 52% above pre-industrial ranges of 280ppm.
Friedlingstein, P. et al. (2024) International Carbon Price range 2024, Earth System Science Information, doi:10.5194/essd-2024-519 (At present revealed as a preprint and so the paper remains to be topic to alter as a part of the peer-review course of.)
Sharelines from this story
