The variety of new coal vegetation underneath growth within the Organisation for Financial Co-operation and Growth (OECD) area has reached document lows because the signing of the Paris Settlement in 2015.
The OECD is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member nations, based in 1961 to stimulate financial progress and international commerce. It contains lots of the world’s wealthiest nations.
In all, the variety of proposed coal vegetation within the OECD area has decreased from 142 in 2015 to 5 right this moment – a 96% fall.
That is in response to the most recent knowledge from World Power Monitor’s World Coal Plant Tracker (GCPT), which incorporates the third quarter (Q3) of 2024.
The GCPT catalogues all coal-fired energy models 30 megawatts (MW) or bigger, with the primary survey relationship again to 2014.
The autumn in proposals places the OECD area properly on its approach to assembly UN secretary-general Antonio Guterres’s 2019 name for “no new coal”, outlined because the cancelling of all unabated coal proposals not already underneath development.
It signifies that one of many 5 remaining proposals may very well be the final new coal-fired energy station to ever be constructed within the OECD.
The OECD and no new coal
Of the 13 OECD nations with coal plant proposals in 2015, all however Turkey have since pledged to cease constructing new coal vegetation.
Certainly, since 2015, proposed coal-fired capability within the OECD has fallen from 142 coal proposals totalling 111 gigawatts (GW) to simply 5 proposals totalling 3GW, GCPT knowledge reveals.
Nevertheless, there are exceptions for coal vegetation that considerably reduce or “abate” carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions by using carbon seize and storage (CCS) expertise.
4 of the 5 proposals – proven within the map beneath – embrace plans for CCS.
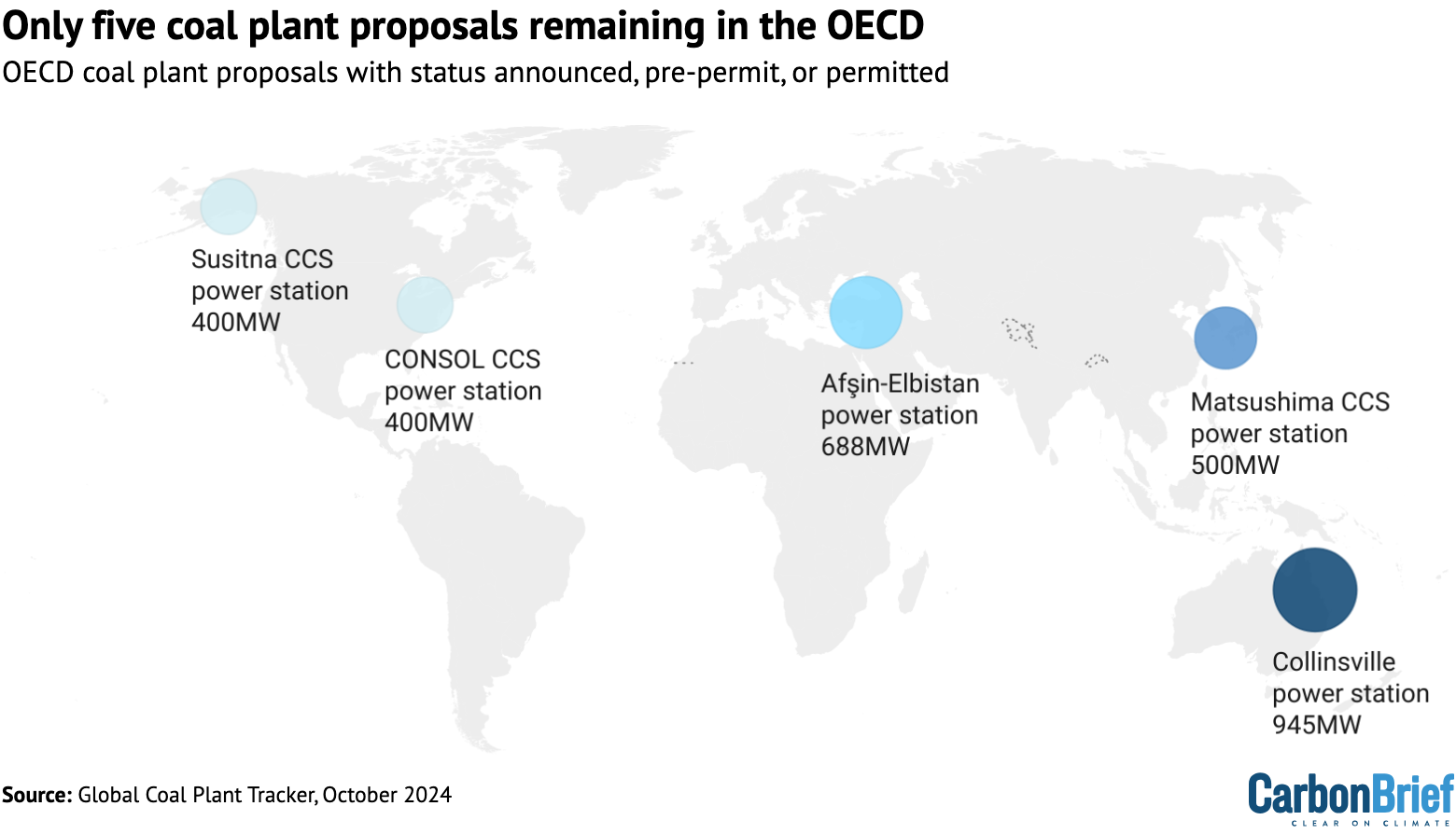
Furthermore, not one of the 5 proposals presently have the required permits for development. This implies it should possible be a number of years earlier than development begins – if they’re constructed in any respect, as many of the proposals within the OECD since 2015 have been deserted totally.
Of the 111GW of recent coal capability that was proposed in 2015, 82% (91GW) has since been shelved or cancelled, in comparison with 17% (19GW) commissioned.
It is a massive a part of the discount within the coal pipeline within the OECD, proven within the determine beneath.
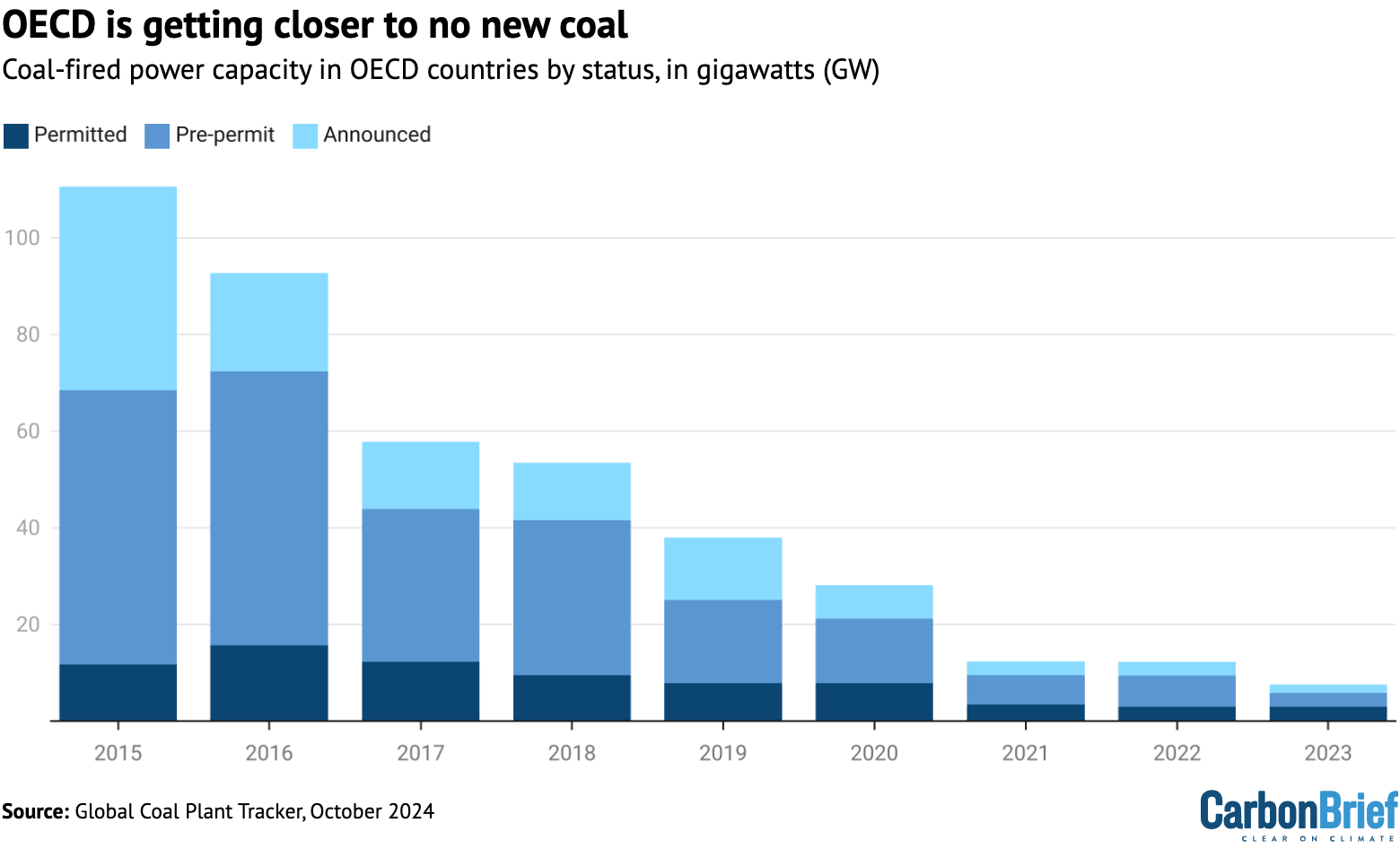
The newest coal vegetation to enter the development part within the OECD broke floor in 2019. Its 1GW of capability stays underneath development right this moment.
The 111GW of proposals in 2015 listed within the GCPT have been positioned throughout 13 nations: Australia, Canada, Colombia, Germany, Greece, Israel, Italy, Japan, Poland, South Korea, Turkey, the UK and the US.
Since 2015, 12 of the 13 nations have pledged assist for no new coal, whether or not as a part of the worldwide Powering Previous Coal Alliance or by a home moratorium on new coal plant permits. The UK phased out coal energy totally this yr.
These commitments to no new coal have been aided by the reducing prices of competing energy sources, together with fuel and – more and more – photo voltaic and wind energy.
Moreover, many nations have seen sustained opposition campaigns to new coal vegetation over the air pollution they’d trigger, their excessive vitality prices and inhabitants displacement.
Because the OECD turns away from new coal, coal energy capability within the area peaked in 2010 at 655GW and has since declined by about one-third to 443GW, as nations shut down ageing coal vegetation.
Turkey resists no new coal
To this point, the federal government of Turkey has resisted calls for no new coal, regardless of repeated rollbacks in its coal plans.
The overwhelming majority of the nation’s proposed coal vegetation have by no means materialised, as proven within the determine beneath.
Particularly, since 2015, greater than 70GW of deliberate coal plant capability in Turkey has been referred to as off, in comparison with 6GW commissioned, translating right into a cancellation price of 92% since 2015. This is without doubt one of the highest cancellation charges on the planet, GCPT knowledge reveals.

Coal plant proposals in Turkey face a myriad of challenges, together with sturdy public opposition over coal plant air pollution and coal trade privatisation. Moreover, home lignite coal is low-quality and unreliable, usually main many vegetation to make use of higher-cost imported coal as an alternative, weakening the financial case for continued reliance on coal.
Within the third quarter of 2024, the licenses for 2 coal vegetation – Karaburun and Kirazlıdere – have been cancelled as a result of irregularities within the environmental allowing course of and the lack of curiosity within the funding by plant sponsors. One other plant, Malkara, was shelved as a result of an absence of exercise, GCPT notes.
The developments have left Turkey with just one coal plant proposal – a exceptional growth after being among the many prime 10 nations with proposed coal-powered capability for practically a decade.
Regardless of this, Turkey has not dedicated to ending new coal plant proposals. Certainly, its lately up to date enhanced local weather plan, referred to as a nationally decided contribution submitted throughout COP29, makes no point out of coal phaseout.
The nation’s remaining proposal is a 688MW two-unit enlargement of the sizable Afşin-Elbistan energy station complicated within the metropolis of Kahramanmaraş.
Native residents have opposed the mission, saying the rise in air pollution within the densely populated metropolis will result in 1000’s of untimely deaths and price billions of {dollars}.
Australia, Japan, the US and ‘clear coal’
The remaining 4 coal plant proposals within the OECD are positioned in Australia, Japan and the US.
Whereas the federal government of Australia lately pledged assist for no new coal and the Japanese and US governments have been a part of the latest G7 dedication to coal phaseout, the three nations additionally assist CCS to minimize or “abate” emissions from coal vegetation.
Abated coal vegetation could also be thought-about suitable with no new coal pledges in the event that they “considerably scale back” carbon emissions sufficient to satisfy Paris-aligned targets.
Critics argue that coal CCS proposals are costlier and polluting than cleaner electrical energy options, usually relying closely on authorities subsidies so as to be economically viable.
Solely a handful of CCS coal vegetation have ever reached business operation – and none have captured as a lot of the ensuing CO2 as they have been focusing on.
The Japanese authorities signed on to a G7 settlement earlier this yr to part out unabated coal energy by the mid-2030s and continues to advertise a set of “clear coal” applied sciences, each domestically and overseas.
The nation’s single remaining coal plant proposal is a brand new coal “gasification” unit at J-Energy’s Matsushima energy station, dubbed GENESIS. The plant would gasify the coal, then co-fire the ensuing gases with biomass, ammonia and hydrogen, earlier than utilizing CCS to abate the ensuing emissions.
Beneath outgoing president Joe Biden, the US additionally signed on to the G7 settlement and was considered one of twelve nations that joined the Powering Previous Coal Alliance throughout COP28 in 2023.
The nation has two Division of Power (DOE)-backed coal-fired energy plant proposals that embrace plans for CCS, as required underneath pending Environmental Safety Company (EPA) rules for brand spanking new coal energy vegetation.
Whereas the way forward for each the coal pledges and rules are unsure, given the latest re-election of Donald Trump, up to now the previous president has been unable to show the tide for coal. Extra coal energy capability was retired underneath Trump’s first time period than both Barack Obama or Biden, and no new coal vegetation have been constructed within the US for over a decade.
Australia’s Labor social gathering voted into energy in 2022 lately joined a COP29 name for no new unabated coal. The nation has not commissioned a brand new coal plant since 2012, with over 13GW of proposed coal-fired capability cancelled since 2010.
The nation’s remaining coal proposal, the Collinsville (Shine Power) energy station, has been touted by its sponsors as a “excessive effectivity, low emissions” (HELE) coal mission with plans to incorporate CCS.
Regardless of these sparse plans for the event of additional coal initiatives, due to this fact, it appears clear that the top is in sight for coal energy within the OECD.
Sharelines from this story
