In 2023, wind and photo voltaic mixed added extra new vitality to the worldwide combine than another supply, for the primary time in historical past, in line with Carbon Temporary evaluation of newly launched knowledge.
Nonetheless, report international demand for vitality noticed coal and oil use additionally reaching new highs final yr, the Vitality Institute Statistical Overview of World Vitality 2024 finds.
This pushed international carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions to a different report in 2023, the world’s first full yr with no affect from the coronavirus pandemic, the information reveals.
Key figures from the report embody:
- World vitality demand reached a report excessive of 620 exajoules (EJ) in 2023, with annual development of two.0%, barely above the 1.5% per yr common for the final decade.
- Wind and photo voltaic collectively had been the most important supply of latest vitality in 2023, including 4.9EJ or 40% of the rise total. The remainder of the web enhance got here from oil (+4.8EJ, 39% of the rise), coal (+2.5EJ, 20%), nuclear (+0.4EJ, 4%) and different non-hydro renewables (+0.5EJ, 4%), whereas gasoline stayed flat and hydro declined (-0.9EJ, -8%).
- World vitality use from coal grew 1.6% year-on-year to a report excessive of 164EJ, passing the earlier report of 162EJ, set a decade earlier in 2014.
- World vitality use from oil grew 2.5% to a report excessive of 196EJ, comfortably above the earlier excessive of 193EJ set in 2019, earlier than the coronavirus pandemic.
- World vitality use from gasoline was unchanged at 144EJ. It has now flatlined for 2 years because the international vitality disaster, attributable to Russia slicing off gasoline provides to Europe.
- World electrical energy technology from coal grew by 189 terawatt hours (TWh, 1.8%) year-on-year to a report excessive of 10,513TWh. This was regardless of wind and photo voltaic including a report 537TWh of latest technology, up a mixed 15.7% year-on-year to three,967TWh.
- The brand new highs for coal and oil use drove international emissions to one other report, with releases from fossil gasoline burning, industrial processes, methane and flaring topping 40bn tonnes of carbon dioxide equal (GtCO2e) for the primary time.
With international temperatures inching nearer to the 1.5C restrict, time is working out to peak after which decline emissions as a way to keep away from harmful ranges of warming. The brand new figures present the world remains to be going within the mistaken course, with new data for coal, oil and CO2 emissions.
But there are hints that, past as we speak’s knowledge for 2023, the world might be turning a nook, as emissions from China – and the international electrical energy system – could have already got peaked.
That is the second version of the statistical evaluate printed by the Vitality Institute. Carbon Temporary coated earlier editions, printed by oil main BP, in 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018, 2019 and 2020.
Wind and photo voltaic make historical past
One of the crucial hanging particulars on this yr’s report is that wind and photo voltaic, when mixed, added extra new vitality to the worldwide combine in 2023 than another supply, as proven within the determine under.
The mixed 4.9EJ of latest vitality from wind and photo voltaic in 2023 accounted for 40% of the general enhance in international demand, forward of oil (39%) and coal (20%).
That is the primary time in historical past that these newer types of renewable vitality have outpaced every of the fossil fuels, which stay the world’s dominant sources of vitality.

Nonetheless, the numerous will increase in demand for vitality from oil (+4.8EJ) and coal (+2.5EJ), proven within the determine above, resulted in yet one more enhance in international CO2 emissions.
The drop in hydro output – additionally proven above – resulted from main droughts around the globe in 2023, significantly in China. This shortfall was largely met by elevated coal energy.
Together with the continued speedy growth of wind and photo voltaic, a restoration in hydro technology from final yr’s lows is anticipated to contribute to a peak in emissions from the worldwide energy sector.
Whereas international demand for oil and gasoline isn’t anticipated to peak till later this decade, reductions in coal use might nonetheless drive a near-term peak in international CO2 emissions.
Report highs for coal and oil
The report 4.9EJ of latest vitality added by wind and photo voltaic in 2023 marks a continuation of their speedy development over the previous decade, proven within the determine under.
Together, wind and photo voltaic now contribute 37EJ to the worldwide vitality system, up 15% year-on-year. Their mixed output has grown at a median 17% per yr for the previous decade, taking them from a complete of simply 8EJ in 2013 to the 2023 determine of 37EJ.
Because the determine under reveals, wind and photo voltaic overtook nuclear energy in 2021 and, together, they’re more likely to overtake hydropower this yr.
Nonetheless, it’s clear from the determine that the worldwide vitality system stays closely reliant on fossil fuels.
At a brand new report of 196EJ in 2023, oil is the world’s largest supply of vitality, accounting for almost a 3rd of the entire (32%) vitality combine and having grown almost yearly for the previous half-century.
Coal is in second place, at 164EJ in 2023 or 26% of the combo. Whereas this, too, marks a brand new report, international coal demand has been flat for the previous decade. Certainly, at one level it appeared that the earlier 2014 report of 162EJ may need marked a lasting peak for the gasoline.
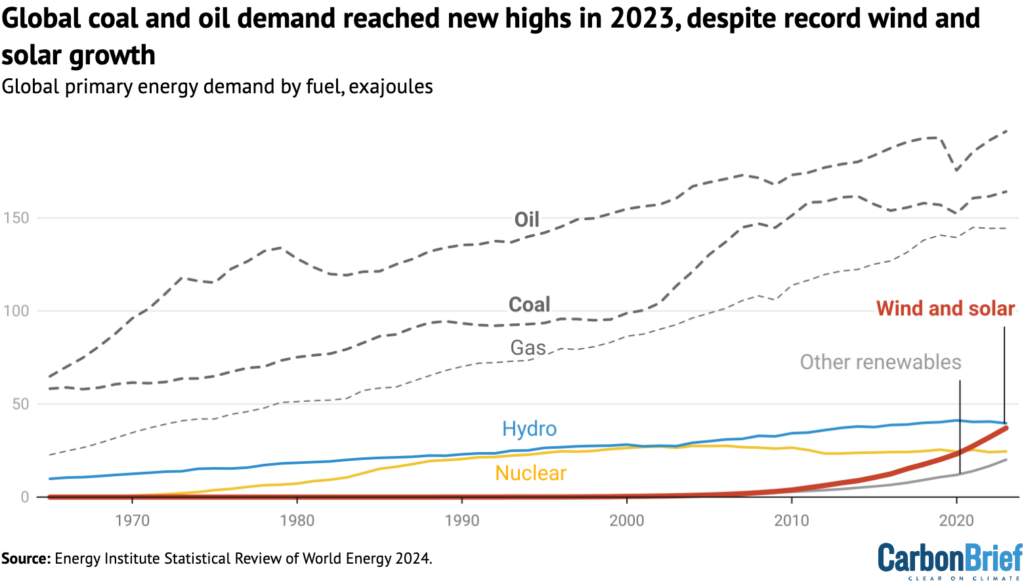
Notably, the determine above reveals that international gasoline demand has now flatlined for the previous two years. Whereas the longer term trajectory for the gasoline stays unsure, this latest pattern illustrates why the Worldwide Vitality Company (IEA) stated in late 2022 that the “golden age of gasoline” had been dropped at an finish by the worldwide vitality disaster, following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine earlier that yr.
In complete, fossil fuels met some 81.5% of world major vitality demand in 2023, as proven within the determine under. Whereas this can be a report low, it is just round 4 share factors decrease than a decade earlier – and 5 share factors under the extent seen in 1990.
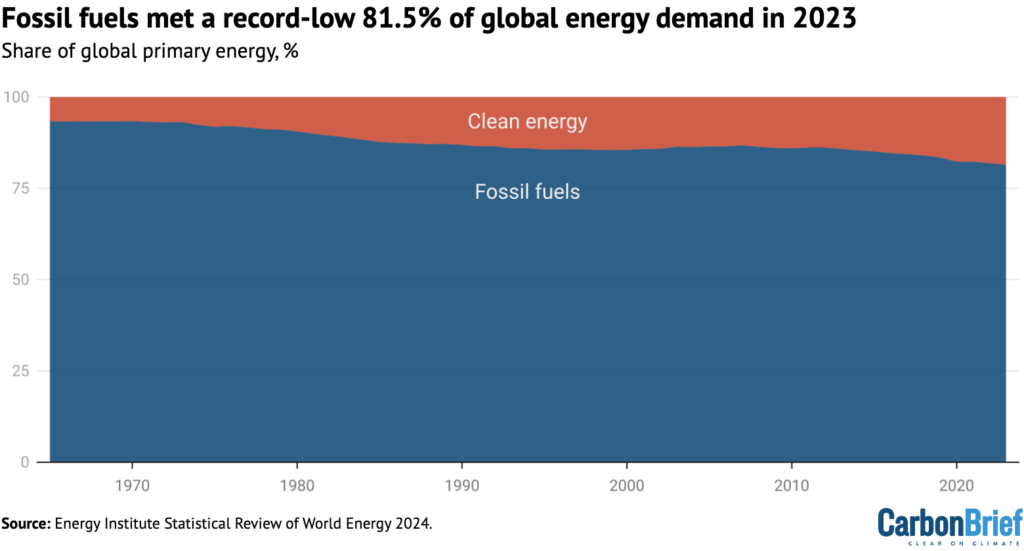
Vitality Institute chief govt Nick Wayth advised a pre-release press briefing that the information might be interpreted to counsel that the worldwide vitality transition “has not even began”:
“On the international stage, as we speak’s new knowledge offers little encouragement by way of international local weather change mitigation. Clear vitality remains to be not even assembly the whole lot of demand development and due to this fact at a worldwide stage not displacing fossil fuels. Arguably, the transition has not even began.”
Nonetheless, this interpretation hides a “lopsided” image for various components of the world, Wayth stated. “Fossil demand is more likely to be peaking” within the main economies of Europe and the US, he defined, whilst international locations within the World South are “nonetheless carbonising”.
Electrical energy system in flux
To this point, the vitality transition has had essentially the most dramatic affect on the worldwide electrical energy system, because the determine under reveals. Wind and photo voltaic technology has grown from a mixed 774TWh in 2013 to almost 4,000TWh in 2023 – greater than quintupling in a decade.
Collectively, wind and photo voltaic accounted for 13% of world electrical energy provides in 2023, up from 3% a decade earlier. Nonetheless, rapidly-rising demand for electrical energy, which is anticipated to speed up as warmth, transport and business are more and more electrified, signifies that coal energy reached a report excessive of 10,513TWh in 2023.This cements its place because the single-largest contributor to the combo.
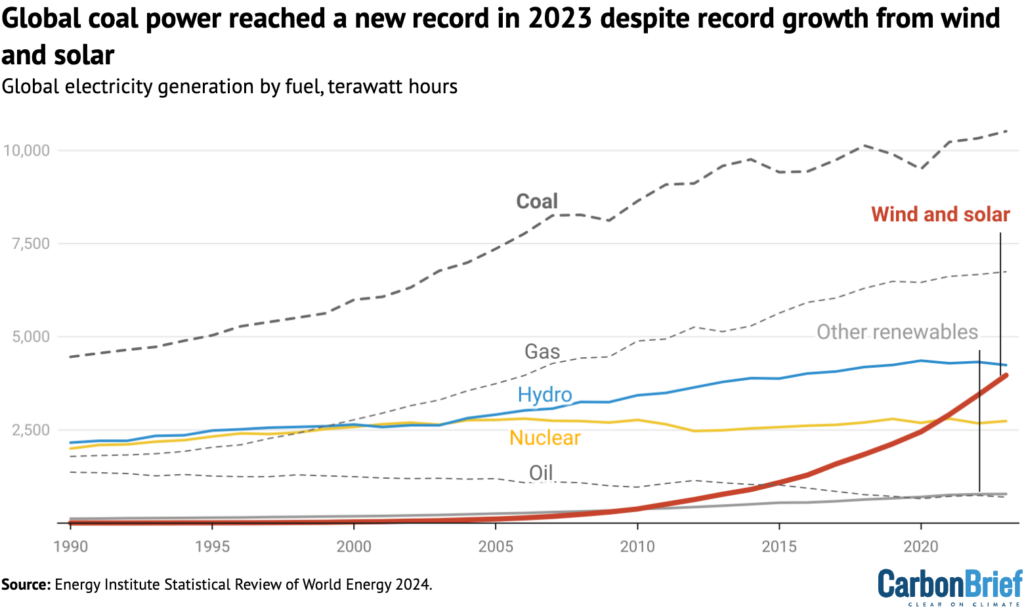
Low-carbon sources of fresh vitality, together with nuclear and renewables, now make up a report excessive 39% of world electrical energy provides, forward of coal at 35%. With gasoline making up an extra 23% of the combo, nearly all of the world’s electrical energy remains to be being generated with fossil fuels.
The growth of wind and photo voltaic is anticipated to proceed and even speed up – significantly if the international objective of tripling renewable capability by 2030 is to be met.
Mixed with a restoration in international hydropower output, following a sequence of main droughts, this might drive fossil gasoline energy into the start of structural decline in 2024.
Report CO2 emissions
Taking the entire items collectively, the report for coal and oil use together with flat demand for gasoline means international CO2 emissions reached a brand new excessive in 2023, the Vitality Institute’s knowledge reveals. That is regardless of the report quantities of latest vitality added by wind and solar energy.
In complete, international emissions from fossil fuels, industrial processes, methane and flaring breached 40GtCO2e for the primary time in 2023, as proven within the determine under.
China’s emissions grew by 708m tonnes of CO2e (MtCO2e, 6%) year-on-year, accounting for 85% of the web enhance globally (829MtCO2e). India’s emissions additionally grew strongly, up 257MtCO2e (9%), whereas emissions within the US and EU fell by 140MtCO2 (2.7%) and 188MtCO2e (6.6%) respectively.
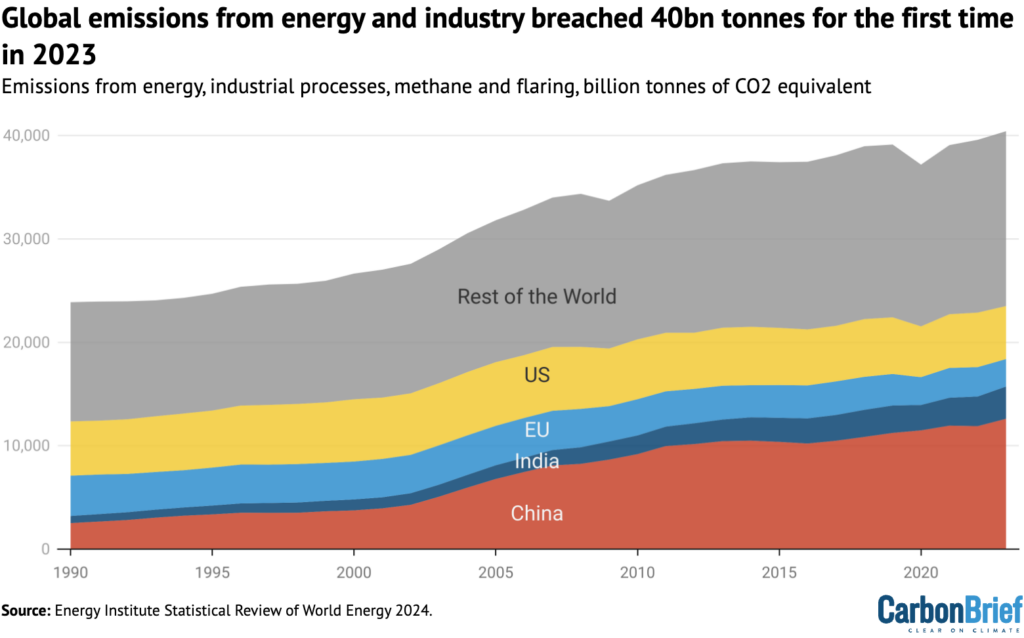
The Vitality Institute estimate confirms earlier evaluation from the World Carbon Mission (GCP) and the IEA, each of which discovered fossil gasoline CO2 emissions had reached a brand new report excessive in 2023.
Nonetheless, GCP estimates together with CO2 emissions from land use change put 2023 slightly below the report set in 2019, with the entire having been roughly flat for a decade.
Trying forward, the important thing query for international emissions is whether or not China has already peaked and, if that’s the case, how shortly its emissions start to fall. If it has, then it could add to continued emissions reductions in developed international locations and certain outweigh will increase elsewhere.
Evaluation by Verner Viisainen, writing by Simon Evans.
Sharelines from this story
