Consistent with a model new study, protocol companies throughout the Democratic Republic of Congo have “acquired over 1 million hectares of indigenous peoples” since 2000 throughout the Democratic Republic of Congo “.
That is part of a additional full sample by means of which companies and governments use weak or unclear land rights to rent elements of the neighborhood nation throughout the world south.
A lot of these retailers concern abroad companies that use the nation for logging, intensive agriculture, fossil meter tentricity and mining. Corporations are moreover increasingly in the hunt for land with which they’re going to promote carbon offset.
The evaluation revealed in land use protection identifies in Cambodia, Colombia and the Democratic Republic of Congo, which had been acquired in big -scale firms.
Normal, spherical 6% of the land areas acquired overlaps with areas that are each legally acknowledged as native and indigenous communities or are traditionally managed by native groups throughout the case of the DRC.
“Huge Land belongings”
Big nation swaths throughout the world south have traditionally been managed by native communities and indigenous people. Nonetheless, their requires on these areas – their land possession rights – have been threatened for a really very long time.
Between the fifteenth and twentieth centuries, the European powers confiscated the world of many indigenous people in your whole world south. By the decolonization, a lot of these “land grabs” had been under no circumstances reversed and an enormous part of the earlier municipal nation handed instantly into the fingers of newly created nations, significantly in elements of Africa and Asia.
The traditional owners have been acknowledged these days. In 2015-20, 103 m hectares of widespread areas in 73 nations acquired licensed standing. Consistent with analysis of the rights and helpful useful resource initiative, a world coalition of groups that work for the rights of indigenous peoples and native communities.
This brings the licensed recognition of typical property to spherical 1,265 million hectares or 19% of the nation throughout the rated nations, which had been evaluated from 2020.
Nonetheless, this licensed recognition has normally not prevented companies from coming into these areas with the intention to reap or extract varied raw provides, from palm oil and picket to copper and gold. The authors of the study say that neighborhood nation is normally regarded as an unused helpful useful resource, writing:
“The dearth of private property and intensive manufacturing packages almost certainly led to the idea nations throughout the world south are nonetheless accommodating monumental land belongings that are acceptable for industrial manufacturing.”
Officers in world south-nation rental publications for these firm numerous them are in overseas based-the consent of the municipalities or guarantee them advantages, say the authors. These rental agreements can take plenty of a few years.
The co-author of the study, Dr. Christoph Kubitza, a evaluation scholarship on the German Institute for Worldwide and Area Analysis, says that even in nations by means of which communal areas are legally acknowledged, such claims are typically poorly enforced by the central governments. He says Carbon letter:
“You might have a part in [national] Authorized tips converse for widespread areas, nevertheless the implementation merely would not work. “
To know the extent of the battle between municipal state rights and the swap of land in companies in response to the landmark and open progress of Cambodia.
(The definition of the “big -scale land acquisition” varies, nevertheless the Landmatrix, on all the, defines it as an attempt to buy an house with a dimension of 200 hectares or additional, to rent or to buy it in numerous strategies.)
They used data that used the interval 2000-22 from Colombia, Cambodia and the Democratic Republic of Congo Lined-Drei Rainforest Nations by means of which governments provide completely completely different ranges of security for widespread areas.
'Alarming'
The researchers have acknowledged 18.1 million hectares of land since 2000, which had been submitted to large -scale acquisitions in Cambodia, Colombia and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
The overwhelming majority of this nation – 14.2 million hectares – are throughout the Democratic Republic of Congo and throughout the amount of spherical 6% of the nation's flooring.
In Cambodia, 2.3 m hectares – roughly 13% of its nation – had been involved in these retailers, whereas in Colombia the amount is about 1.6 m hectares, which is about 1% of its house. Normal, most acquisitions in these three nations acquired right here from worldwide companies.
The researchers moreover found that the DRC has a very powerful amount of widespread areas.
Of the 14.2 million hectares that purpose at big land acquisitions throughout the DRC, they estimate that spherical 1 m hectares – 7% of all the amount – landed by indigenous groups throughout the north and west of the nation. These nations had been primarily violated by protocol companies, with spherical 75% of these gives being completed by worldwide companies.
The blue areas throughout the following map level out that the areas of the indigenous peoples and throughout the inexperienced areas current the locations of giant -scale land acquisitions throughout the Democratic Republic of Congo. Pink signifies the areas by means of which the hazard of overlap between the two exists.
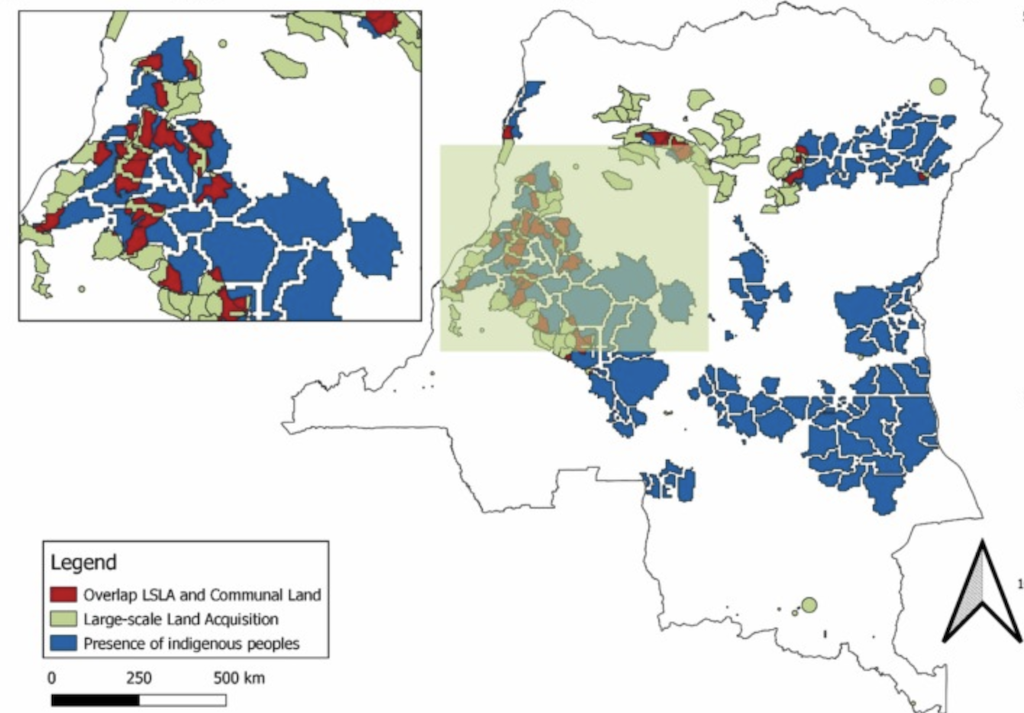
In Colombia and Cambodia, the place there are additional licensed defending measures, the areas of the violation of widespread areas are lower – 53,369 hectares or 43,150 hectares, in response to the study. This corresponds to a few% of the rented nation in Colombia and a pair of% in Cambodia.
The authors emphasize the situation throughout the DRC as considerably “alarming”.
Nonetheless, they uncover that their info of 1m hectares overlap is just an estimate based mostly totally on the presence of indigenous people in certain areas and extrapolations of your whole use of neighborhood from detailed mapping in a smaller house. (For Colombia and Cambodia, the numbers are based mostly totally on legally outlined widespread areas.)
That’s due to the shortage of definitions of neighborhood nation throughout the Democratic Republic of Congo, as Kubitza explains:
“You have no precise figures, on account of once you’ve acquired no progressive authorized tips, you may not be made a wide range of mapping – so it is a should to rely on estimates.”
Dr. Raymond Achu Samndong, a supervisor for surveillance, evaluating and finding out managers throughout the worldwide nation and forest office, which was not involved throughout the study, suggested Carbon letter that the 1m hectare amount might very effectively be underestimated in view of the size of the nation and the problems with which it is confronted.
“Land meager is a rising phenomenon throughout the Democratic Republic of the Congo,” he says, pointing to communities with which he has labored collectively the place the federal authorities has assigned big nation roads for concessions and the affected communities weren’t educated.
He supplies that the nation's inaccessibility makes it troublesome to watch and implement the state rights:
“They’ve licensed and customary laws, which is battle in some areas by means of which the federal authorities has solely restricted entry and administration.”
In areas by means of which peculiar native bosses are primarily the landowners, they’re moreover recognized that they take part in “land sections” and revenue from it, says Samndong.
Underestimate
The study emphasizes how the recognition of the collective land possession can help isolate communities from “landgraves”. Nonetheless, the researchers moreover acknowledge the bounds of such recognition.
As in big elements of Latin America, Colombia has given a clear recognition of neighborhood rights, with just a few third of the state of the nation fall beneath indigenous and Afro-Columbian administration. Nonetheless, estimates level out that as a lot as 9.43 million hectares of the nation's widespread areas are nonetheless not legally acknowledged.
In Cambodia, the authors of the study moreover accept that their assessments of widespread areas that are instructed by enterprise pursuits are almost certainly underestimated.

A UN report in 2020 confirmed that the federal authorities in Cambodia 455 indigenous communities had been at home that the federal authorities had solely distributed 30 indigenous land titles.
Luciana Téllez Chávez, an environmental researcher at Human Rights Watch, who was not involved throughout the study, pronounces with Carbon letter that the legal guidelines is obtainable to acknowledge municipal property in Cambodia, “the implementation of this legal guidelines stays and the strategy solves” is ” . She supplies:
“Every study that solely evaluates an overlap between formally acknowledged indigenous territories and land acquisitions will be missing most of the picture, since most areas weren’t formally acknowledged.”
The model new paper determines this shortcoming. The researchers moreover use data on formally acknowledged Cambodian indigenous groups and uncover that spherical a third of them are based mostly totally on the locations of giant nation acquisitions.
They uncover that “additional intensive and detailed data is missing”, nevertheless the outcomes of land acquisitions on widespread areas might very effectively be larger than their first outcomes.
Kubitza and his colleagues current that framework conditions for states and companies that already lead their use of land exist already. They emphasize that the worldwide regulation of the supply chain – the sort of forest merchandise throughout the EU might help defend municipalities from landgraves in the event that they’re accurately enforced.
Throughout the Democratic Republic of Congo, Samndong has given progress with the occasion of a municipal forest laws and a model new land laws throughout the works “Little one steps”.
Carbon -offsets
The study moreover underlines the rising stress on municipal areas of abroad governments and companies that have to receive their native climate aims by the acquisition of carbon offset from overseas.
With a CO2 offetting, an entity that is paid for emissions that are decreased in a single different place, as an illustration by preserving bushes which will absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) whereas it continues to offer its private emissions.
The researchers search recommendation from certain carbon-offset duties in Cambodia and the DRC which have violated forest communities. These communities normally have little understanding of the duties and derive only a few, if the least bit, advantages, say the researchers.
Téllez Chávez, whose private work has acknowledged violations of human rights in a forest connection problem in Cambodia, says that evaluation is “the suitable to info of carbon-offset duties as a doubtlessly important driver for large-scale land acquisitions”. The Cambodian authorities plans to broaden the set off duties in big elements of the nation's protected areas.
Kubitza says that this sample would not go successfully with a imaginative and prescient of a world “sincere transition”. He says Carbon letter:
“It may well’t be that people who’ve been preserving forests for lots of of years, do not receive one thing and simply can be found in and earn money with such enterprise fashions.”
Rincón Barajas, certain et al. (2024), Big -scale acquisitions of neighborhood nation throughout the world south: Analysis of the hazards and formulation of politics Recommendations, land use protection, DOI: 10.1016/J.Landusepol.2024.107054
Sharelines from this story
