The Earth is on a “disastrous trajectory” with “no enough international governance” to take care of the dimensions of threats posed by local weather tipping factors, warns a serious new report.
These tipping factors “pose among the gravest threats confronted by humanity”, based on the authors.
They establish greater than 25 tipping factors throughout the Earth system, starting from ice-sheet collapse to rainforest dieback.
“5 main tipping factors are already vulnerable to being crossed because of warming proper now and three extra are threatened within the 2030s because the world exceeds 1.5C international warming,” the report finds.
Crossing Earth system tipping factors would have “catastrophic” impacts on societies, with the potential to “escalate violent conflicts, mass displacement and monetary instability”, the report additionally warns.
The authors say that selling “optimistic social tipping factors” in socio-behavioural, technological, financial and political programs is “the one reasonable systemic danger governance possibility” to restrict the dangers.
Many optimistic tipping factors have already been crossed – comparable to renewable vitality turning into the most affordable type of electrical energy in some international locations, and electrical autos gaining the biggest share of the market in others – the report finds.
A global staff of greater than 200 researchers have contributed to this report, which was initiated at a convention on tipping factors in September 2022. (See Carbon Temporary’s protection of the occasion.) The report was funded by the Bezos Earth Fund.
The authors of the report help a proposal – presently into consideration – for the Intergovernmental Panel on Local weather Change (IPCC) to organize a particular report on the subject of tipping factors.
In addition they name for the dangers and alternatives round tipping factors to be included within the international stocktake of progress in the direction of the objectives of the Paris Settlement, in addition to future revisions of Nationally Decided Contributions and nationwide and sub-national coverage measures.
On this Q&A, Carbon Temporary unpacks the report’s findings on “unfavourable” Earth system tipping factors and “optimistic” social tipping factors.
What are tipping factors?
Scientists have warned for many years that many Earth programs are vulnerable to crossing “tipping factors” – vital thresholds that, if exceeded, may push a system into a completely new state.
Prof Tim Lenton is the chair of local weather change and Earth system science on the College of Exeter and lead writer of the brand new report on “international tipping factors”. He describes a tipping level as when “a small change makes a giant distinction and adjustments the state or the destiny of a system”.
The report makes use of the analogy of a ball in a valley to explain tipping factors, as proven within the graphic under.
Within the left-most panel (blue), the ball sits within the left-side valley. If the ball is given a small push, it rolls briefly up the aspect of the valley earlier than returning to its beginning place. This “resilience” – the system’s means to face up to adjustments – exhibits that the system is secure, the report says.
Nevertheless, the report warns that human exercise – together with local weather change, ecosystem degradation and air pollution – are making many Earth programs much less secure. That is proven by the left-hand valley getting shallower within the center panel (purple) and the reducing of the hill between it and the right-hand valley. Now it will be simpler for the ball to maneuver into the right-hand valley when pushed.
As a system comes near a tipping level, it could be slower to return to its unique state after a “perturbation” or disturbance, the report says. This might be proven by the ball returning extra slowly to its unique place after it’s pushed.
Dr David McKay – an unbiased analysis marketing consultant and visiting fellow on the College of Exeter’s International Programs Institute – is a bit lead on the brand new report. He describes this behaviour as a “wobble” and tells a press briefing that it will possibly typically be picked up utilizing observational information. That is vital, as a result of it will possibly present an early warning sign {that a} tipping level is approaching.
A “tipping level” is crossed when the ball rolls previous the purpose of no return into the right-side valley, leaving its unique state and settling into a brand new secure state. That is proven within the right-hand panel (pink). It’s now very troublesome for the ball to return to its unique state within the left-hand valley.
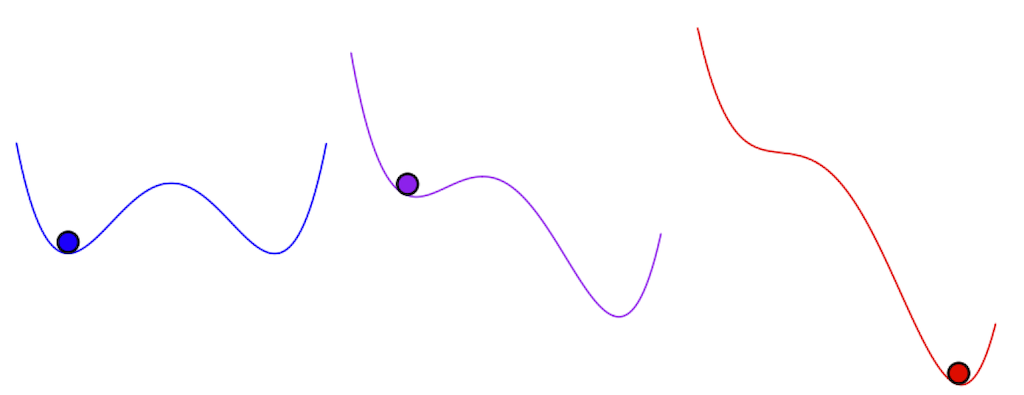
The report says {that a} tipping level happens “when change in a part of a system turns into self-perpetuating past a threshold, resulting in substantial, widespread, ceaselessly abrupt and sometimes irreversible influence”.
Beneath this definition, additionally it is attainable for tipping factors to be reversible and “non-abrupt” – though this isn’t normally the case, the authors observe.
What are the primary Earth system tipping factors?
Lately, there was loads of educational dialogue about which parts of the Earth system may exhibit tipping factors.
The report synthesises tons of of peer-reviewed articles to establish greater than 25 elements of the Earth system which have tipping factors throughout the cryosphere, biosphere, environment and oceans. (Carbon Temporary has beforehand unpacked 9 of them intimately.)
Importantly, the authors additionally present which programs they don’t consider to exhibit tipping behaviour.
Cryosphere
The report identifies a number of tipping factors within the cryosphere, as proven on the map under.
The colors and markers point out how assured the authors are that every system has a tipping level. A pink bar and “+++” marker signifies that the authors are very assured that the system is a tipping level. A blue bar and “- – -” marker signifies that the authors are very assured that the system isn’t a tipping level. The 4 arrows and globe symbols point out regional and international programs, respectively.
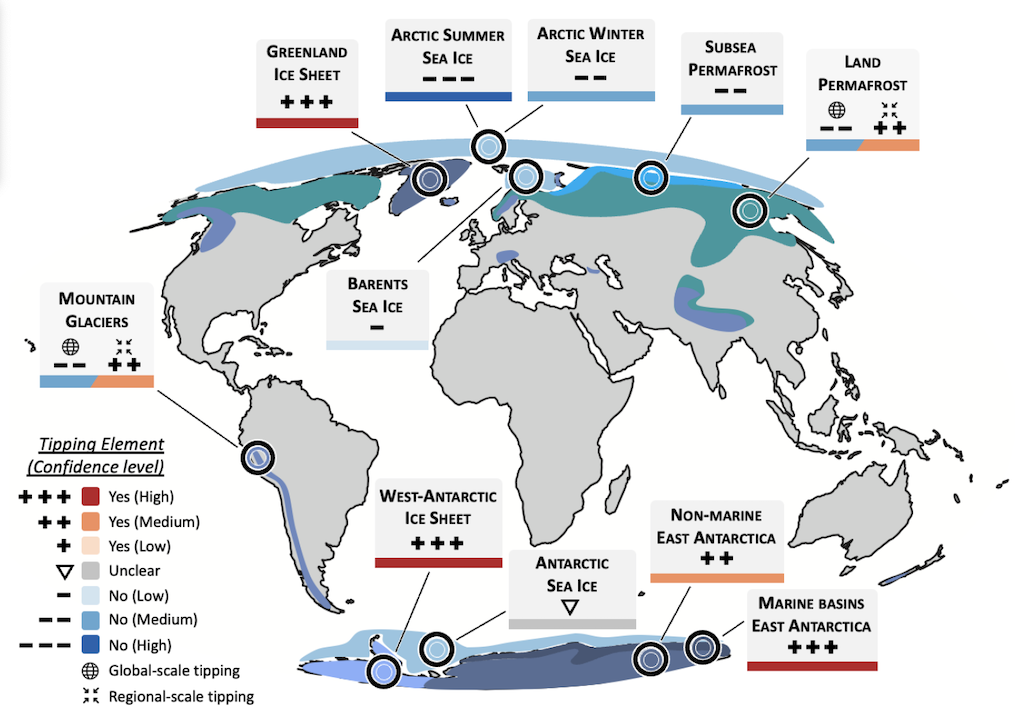
There are “a number of traces of proof” to help the existence of “large-scale” tipping factors from the melting of the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets, the report says, explaining that if ice loss exceeds a threshold quantity, self-amplifying feedbacks may trigger the ice to disintegrate even quicker, resulting in large-scale ice-sheet “collapse”.
Conversely, the authors have “excessive confidence” that Arctic summer season sea ice loss isn’t a tipping system, discovering that in fashions and observations, summer season sea ice loss tends to extend “progressively, however absolutely” consistent with warming.
In the meantime, the authors discover proof for “localised and regional” tipping factors in glaciers and permafrost, however discover that these programs don’t exhibit “large-scale tipping dynamics”.
Oceans and environment
There are 4 additional tipping factors within the oceans and environment, together with monsoons over west Africa, India and South America, clouds and El Niño southern oscillation (ENSO), based on the report. These are proven within the map under.
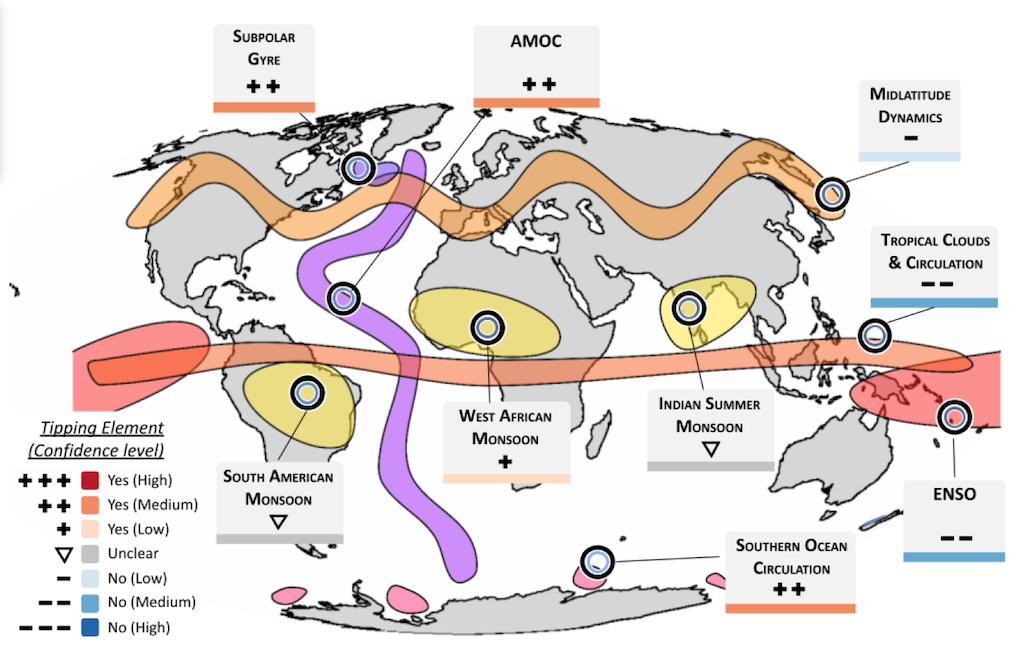
The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) is a serious system of ocean currents that performs an vital position in regulating the worldwide local weather. The report explains that rising temperatures, mixed with an inflow of chilly, recent water from the melting of the Greenland ice sheet, may destabilise these ocean currents, doubtlessly inflicting the complete system to “shut down”.
Equally, the authors discover proof for tipping factors within the overturning circulations within the Atlantic and the Southern oceans, in addition to for the west African monsoon.
The authors additionally assess the literature on cloud-induced tipping factors. Numerous completely different mechanisms linked to incoming photo voltaic radiation and outgoing infrared radiation have been urged, however the authors conclude that “concern about cloud-driven tipping factors is comparatively low”.
Biosphere
The report finds probably the most tipping factors within the biosphere, as proven within the map under. Totally different colors of shading point out completely different biomes – for instance, coral reefs in pink and mangroves in pink.
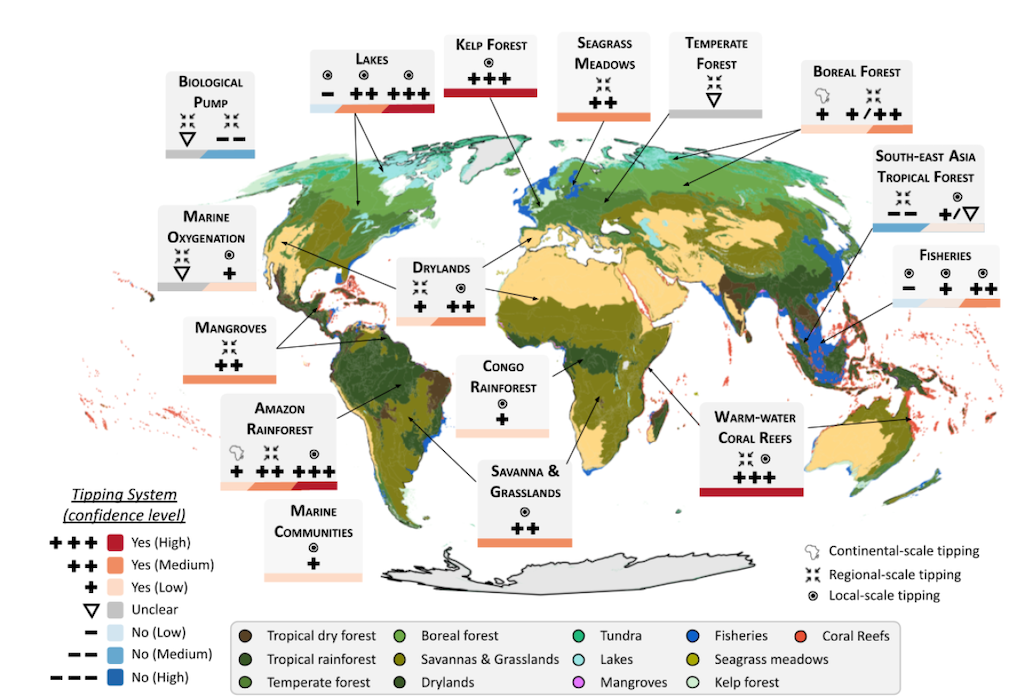
Programs within the biosphere have extra “co-drivers” that may scale back their resilience – comparable to local weather change, habitat loss and air pollution – making tipping factors simpler to succeed in, the report finds.
For instance, it notes that the Amazon supplies a lot of its personal rainfall by biking water between the environment and vegetation. Deforestation and local weather change can disrupt this mechanism, pushing the system over a tipping level the place it turns from forest into savannah. This course of is known as forest “dieback”.
Amongst tropical forests, there’s most proof of a tipping level for the Amazon, the report finds. Different tropical forests such because the Congo have proof for native tipping factors, however are much less more likely to cross them, the report finds.
The authors additionally discover that mangroves and sea grasses – that are “traditionally among the many most human-threatened ecosystems on this planet” – are in danger tipping regionally. They spotlight regional examples of “mangrove die-off”, which generally happen when the mangroves are “physiologically careworn”.
The report additionally seems at marine meals webs and fisheries, discovering that “marine group shifts happen when abrupt adjustments cascade via a number of species or purposeful teams of an ecosystem”.
When may key thresholds be crossed?
Assessing when key local weather tipping factors could also be crossed has been a key space of analysis for a few years. One option to establish imminent tipping factors is by on the lookout for the “wobble” or “lack of resistance” in a system.
For instance, the report cites analysis that finds three-quarters of the Amazon rainforest has misplaced “resilience” since 2003, making it slower to get well from droughts and heatwaves. This means that the forest could possibly be approaching a tipping level, the authors say.
Components of the Greenland ice sheet and AMOC are additionally exhibiting a lack of resilience, the report finds. It provides that given present-day warming of 1.2C, tipping of warm-water coral reefs is probably going:
“Coral reefs are already experiencing tipping factors, as extra frequent warming-driven bleaching occasions, together with air pollution, excessive climate occasions and ailments, tip them to degraded algae-dominated states.”
Because the planet continues to heat, the chance of crossing key thresholds will increase. The report additionally attracts on analysis just lately revealed by McKay, which assesses what number of tipping factors could possibly be triggered at completely different ranges of worldwide warming.
The higher half of the plot under exhibits the chance of triggering 15 tipping parts at completely different temperature ranges. Yellow signifies a low chance and pink signifies a excessive chance, whereas the dotted line signifies a central estimate.
The gray line beneath exhibits noticed warming to the current day and projections out to 2100 from 1.5C (inexperienced) to greater than 4C (pink). The gray shading within the higher chart signifies anticipated warming given present local weather insurance policies.
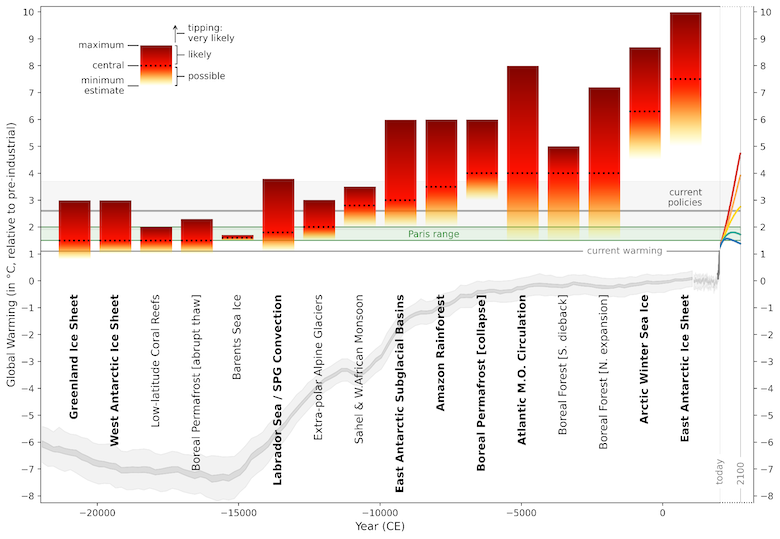
The report says that 5 completely different tipping factors are already “vulnerable to being crossed because of warming proper now”. These are Greenland and West Antarctic ice sheet collapse, warm-water coral reef die-off, widespread localised abrupt thaw in permafrost and overturning circulation collapse within the North Atlantic subpolar gyre.
The North Atlantic subpolar gyre is a counter-clockwise ocean present to the south of Greenland, which drives the oceanic currents and redistributes warmth and freshwater within the excessive latitude North Atlantic. The gyre is a element of AMOC, and is taken into account as a main tipping component of the local weather system.
The report provides that three extra tipping factors are vulnerable to being crossed within the 2030s because the world exceeds 1.5C above pre-industrial temperatures.
Nevertheless, the report warns that key thresholds could possibly be crossed “at decrease ranges of worldwide warming than beforehand thought”, including:
“Our greatest fashions probably underestimate tipping level dangers. The world is basically flying blind into this huge risk.”
This underestimation is basically because of “patchy and fragmented” information, the authors say. For instance, they observe that “typical modelling approaches battle to precisely symbolize ice sheet dynamics”.
The authors of the report help a proposal for the IPCC to organize a particular report on the subject of tipping factors. The proposal was put ahead by Switzerland in Could 2022 and is presently into consideration.
What are the impacts of crossing tipping factors?
The impacts of crossing Earth system tipping factors “could possibly be catastrophic”, the report warns.
Melting of the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets would endanger coastal communities, and will result in the entire lack of many small island nations, the report finds. Antarctic ice sheet instability alone may result in a possible sea degree rise of two metres by 2100, exposing 480 million individuals to annual coastal flooding occasions, it says.
Amazon dieback can be a “disaster for biodiversity”, the report finds. Lowered river circulate would result in transport difficulties within the area, and a few six million individuals would face “excessive warmth stress danger”. Total, the report estimates {that a} full Amazon dieback would trigger damages of between $1tn and $3.5tn.
Thawing permafrost causes the bottom to grow to be unstable or “stoop”, and the report warns that 70% of present infrastructure in permafrost areas is in areas with “excessive potential for thaw by 2050”.
It provides that crossing a tipping level within the AMOC would result in international adjustments in rainfall patterns, with implications for water safety and crop manufacturing world wide. The nice and cozy water that the AMOC carries northwards releases warmth into the environment, which implies it performs a vital position in preserving Western Europe heat.
Nevertheless, the Earth system tipping factors don’t act in isolation. The authors discover that crossing some tipping factors, such because the dieback of rainforests or thawing of permafrost, releases extra CO2 into the environment, inflicting additional warming.
Moreover, many Earth programs are interlinked, that means that crossing one tipping level can enhance the chance of crossing others. The authors describe this as a “domino impact” or “tipping cascade”.
The map under exhibits these interactions. Purple arrows point out that crossing one tipping level causes one other system to grow to be extra unstable, making it extra more likely to tip. Blue arrows point out the alternative. Gray arrows point out unclear results.
Programs that will not tip on their very own – however are nonetheless vital because of their interactions with different programs – are proven with a blue outer circle. Tipping programs that exert a notable suggestions on international common temperature once they tip are denoted by a pink inside ring.
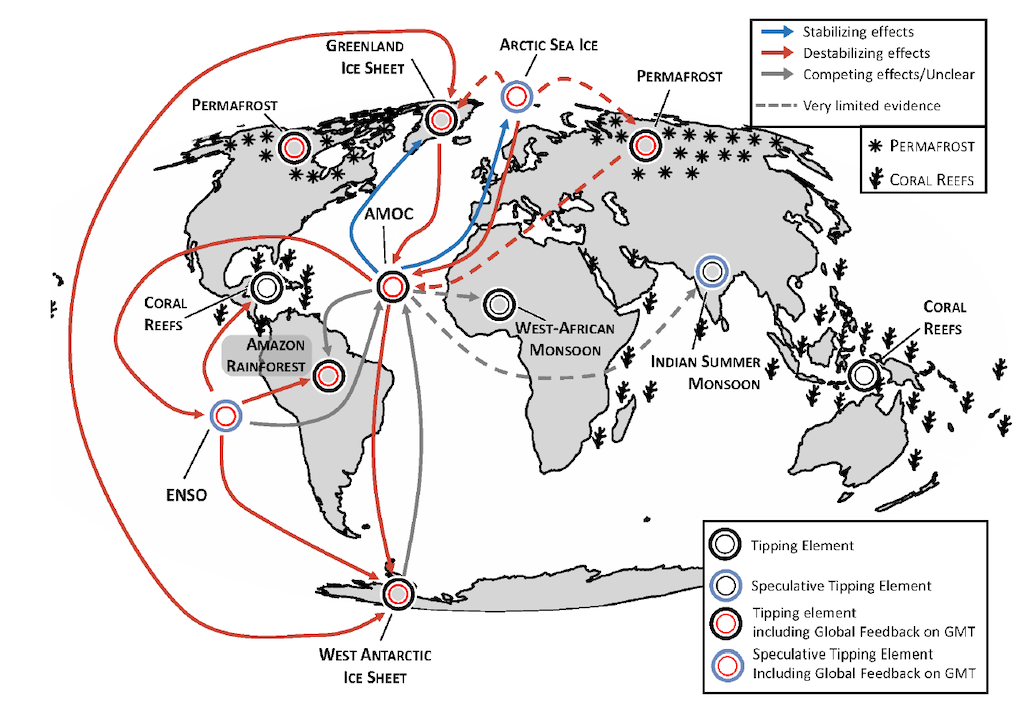
The report finds that almost all of interactions between local weather tipping programs are destabilising – indicating that crossing one tipping level will usually result in additional tipping factors being crossed.
For instance, disintegration of the Greenland ice sheet would lead to giant volumes of cool freshwater flowing into the ocean, which may push the AMOC past a tipping level. This, in flip, may result in an intensification of ENSO, which may go on to affect climate patterns over the Amazon, inflicting rainforest dieback, the report explains.
Crossing key tipping factors “may have catastrophic impacts on human societies”, together with a rise in violence and battle, large-scale displacement and monetary destabilisation, the authors warn.
The report says that Earth system destabilisation may result in “social cohesion breaking down”, driving a rise in “psychological issues”, in addition to “higher radicalisation of varied teams and polarisation, making it tougher to search out collective options”. The report provides:
“These impacts may escalate to threaten the breakdown of financial, social and political programs, triggering damaging tipping factors in societies experiencing stresses past their means to manage.”
The authors add that every time a tipping level is crossed, humanity will probably be compelled to divert extra consideration and sources into catastrophe response, “eroding away a few of our company
to sort out the underlying drivers”. This in flip would make it extra probably for extra tipping factors to be crossed sooner or later, making a “vicious cycle”, they are saying.
Can ‘optimistic tipping factors’ mitigate the dangers?
“The existence of tipping factors implies that ‘enterprise as common’ is now over,” the report warns. It provides:
“Speedy adjustments to nature and society are occurring, and extra are coming. If we don’t revise our governance strategy, these adjustments may overwhelm societies because the pure world quickly comes aside.”
Nevertheless, the authors add that “presently, there isn’t any enough international governance on the scale of the threats posed by unfavourable tipping factors”.
The authors argue that “optimistic social tipping factors” – feedbacks in socio-behavioural, technological, financial and political programs that set off a optimistic change – could possibly be “the one reasonable systemic danger governance possibility” to restrict the dangers.
Lenton advised the press briefing that humanity has “left it principally too late for incremental motion on the local weather disaster”, including that optimistic tipping factors are key to limiting harmful ranges of warming.
Many optimistic social tipping factors are being reached or have already been crossed, the authors say.
For instance, they are saying that renewable vitality has reached a tipping level of price parity with fossil-fuelled energy era. They add that electrical autos “present proof of passing or approaching tipping factors in main markets together with China and Europe”.
Dr Tom Powell – a analysis influence fellow at Exeter’s International Programs Institute and part lead on the report – advised the press briefing that “the extra of one thing we construct, the cheaper it will get to construct”.
He referred to as this a “highly effective reinforcing suggestions”, including that it’s answerable for a few of these price reductions and renewable energies and electrical autos.
In an analogous option to unfavourable Earth system tipping factors, one optimistic social tipping level can set off one other, resulting in a domino or cascade that generates “widespread societal change”, the authors say. Lenton outlined a optimistic tipping cascade in electrical automobile manufacture:
“As electrical autos cross the optimistic tipping level of market dominance, this produces a lot of low cost batteries, and people low price batteries are essential to supply important storage capability to strengthen a distinct optimistic tipping level in the direction of renewable vitality for our energy provide.
“And that may in flip set off optimistic tipping factors in producing inexperienced ammonia and inexperienced hydrogen fuels for fertiliser, transport and so forth.”
Powell provides that “social contagion is a very highly effective power”, noting that “the extra individuals round you who’re adopting sustainable selections, the extra probably you’re to take action your self”. He provides:
“The extra seen sustainable selections are among the many normal inhabitants, the better it turns into for politicians to make coverage selections which may have appeared very troublesome just a few years in the past.”
Nevertheless, optimistic social tipping factors “don’t simply occur by magic”, Lenton advised the press briefing. As an alternative, he mentioned they want “coordinated motion”.
The report’s authors name for Earth system tipping level dangers, corresponding motion and optimistic tipping level alternatives to be included within the international stocktake underneath the Paris Settlement, in addition to future revisions of Nationally Decided Contributions (NDCs) and nationwide and sub-national coverage measures.
The latest iteration of the international stocktake textual content mentions local weather tipping factors twice. In a single, it invitations the scientific group to:
“Generate info related for NDCs and aligning them with 1.5C, cross-cutting issues comparable to tipping factors, steerage on dangers and impacts, vulnerability, cryosphere and shutting statement gaps.”
Dr Manjana Milkoreit – a postdoctoral fellow on the College of Oslo and part lead on the report – provides that selections and actions taken within the coming a long time will commit us to “actually long-term adjustments”, including that the difficulty of tipping factors is vital for our notions of intergenerational justice.
Sharelines from this story
